Frequency control of cell cycle oscillators
- PMID: 20851595
- PMCID: PMC3522487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2010.08.006
Frequency control of cell cycle oscillators
Abstract
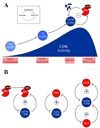
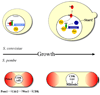
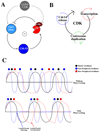
The cell cycle oscillator, based on a core negative feedback loop and modified extensively by positive feedback, cycles with a frequency that is regulated by environmental and developmental programs to encompass a wide range of cell cycle times. We discuss how positive feedback allows frequency tuning, how size and morphogenetic checkpoints regulate oscillator frequency, and how extrinsic oscillators such as the circadian clock gate cell cycle frequency. The master cell cycle regulatory oscillator in turn controls the frequency of peripheral oscillators controlling essential events. A recently proposed phase-locking model accounts for this coupling.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Tyson JJ, Chen KC, Novak B. Sniffers, buzzers, toggles and blinkers: dynamics of regulatory and signaling pathways in the cell. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:221–231. - PubMed
-
- Felix MA, Labbe JC, Doree M, Hunt T, Karsenti E. Triggering of cyclin degradation in interphase extracts of amphibian eggs by cdc2 kinase. Nature. 1990;346:379–382. - PubMed
-
- Dunlap JC, Loros JJ, Colot HV, Mehra A, Belden WJ, Shi M, Hong CI, Larrondo LF, Baker CL, Chen CH, et al. A circadian clock in Neurospora: how genes and proteins cooperate to produce a sustained, entrainable, and compensated biological oscillator with a period of about a day. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:57–68. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

