Crosstalk between VEGFR2 and muscarinic receptors regulates the mTOR pathway in serum starved SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells
- PMID: 20851763
- PMCID: PMC2956770
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.09.008
Crosstalk between VEGFR2 and muscarinic receptors regulates the mTOR pathway in serum starved SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
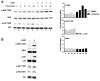
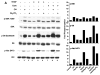
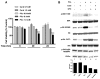
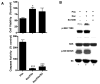
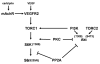
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAchRs) are guanosine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein) coupled receptors that crosstalk with receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) to signal mitogenic pathways. In particular, mAchRs are known to couple with RTKs for several growth factors to activate the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)/Akt pathway, a regulator of protein synthesis. The RTK for the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGFR2, can signal protein synthesis but whether it cooperates with mAchRs to mediate mTOR activation has not been demonstrated. Using serum starved SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells, we show that the muscarinic receptor agonists carbachol and pilocarpine enhance the activation of the mTOR substrate p70 S6 Kinase (S6K) and its target ribosomal protein S6 (S6) in a VEGFR2 dependent manner. Treatments with carbachol increased VEGFR2 phosphorylation, suggesting that mAchRs stimulate VEGFR2 transactivation to enhance mTOR signaling. Inhibitor studies revealed that phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase resides upstream from S6K, S6 and Akt phosphorylation while protein kinase C (PKC) functions in an opposing fashion by positively regulating S6K and S6 phosphorylation and suppressing Akt activation. Treatments with the phosphatase inhibitors sodium orthovanadate and okadaic acid increase S6, Akt and to a lesser extent S6K phosphorylation, indicating that tyrosine and serine/threonine dephosphorylation also regulates their activity. However, okadaic acid elicited a far greater increase in phosphorylation, implicating phosphatase 2A as a critical determinant of their function. Finally, pilocarpine but not carbachol induced a time and dose dependent cell death that was associated with caspase activation and oxidative stress but independent of S6K and S6 activation through VEGFR2. Accordingly, our findings suggest that mAchRs crosstalk with VEGFR2 to enhance mTOR activity but signal divergent effects on survival through alternate mechanisms.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Okadaic acid induces Akt hyperphosphorylation and an oxidative stress-mediated cell death in serum starved SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells that are augmented by rapamycin.Neurosci Lett. 2012 Dec 7;531(2):74-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.10.052. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Neurosci Lett. 2012. PMID: 23127854 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of mTOR-dependent S6 phosphorylation by muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Aug 1;104(5):1818-31. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21745. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18348264
-
Muscarinic-receptor-mediated inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-stimulated phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells.Biochem J. 2004 May 1;379(Pt 3):641-51. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031700. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14769130 Free PMC article.
-
p70 S6 kinase as a therapeutic target in cancers: More than just an mTOR effector.Cancer Lett. 2022 Jun 1;535:215593. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215593. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35176419 Review.
-
TOR action in mammalian cells and in Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004;279:115-38. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-18930-2_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14560955 Review.
Cited by
-
Short-term regulation of murine colonic NBCe1-B (electrogenic Na+/HCO3(-) cotransporter) membrane expression and activity by protein kinase C.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 18;9(3):e92275. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092275. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24642792 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the β-common receptor by erythropoietin impairs acetylcholine-mediated vasodilation in mouse mesenteric arterioles.Physiol Rep. 2018 Jun;6(12):e13751. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13751. Physiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29939494 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling through the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor VEGFR-2 protects hippocampal neurons from mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Oct;63:421-31. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.036. Epub 2013 May 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23732519 Free PMC article.
-
Okadaic acid induces Akt hyperphosphorylation and an oxidative stress-mediated cell death in serum starved SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells that are augmented by rapamycin.Neurosci Lett. 2012 Dec 7;531(2):74-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.10.052. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Neurosci Lett. 2012. PMID: 23127854 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms differentially protect neurons against neurotoxic events associated with Alzheimer's disease.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Jun 27;16:1181626. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1181626. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37456522 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

