The neural organization of semantic control: TMS evidence for a distributed network in left inferior frontal and posterior middle temporal gyrus
- PMID: 20851853
- PMCID: PMC3077429
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhq180
The neural organization of semantic control: TMS evidence for a distributed network in left inferior frontal and posterior middle temporal gyrus
Abstract
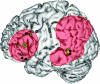
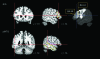
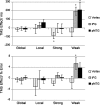
Assigning meaning to words, sounds, and objects requires stored conceptual knowledge plus executive mechanisms that shape semantic retrieval according to the task or context. Despite the essential role of control in semantic cognition, its neural basis remains unclear. Neuroimaging and patient research has emphasized the importance of left inferior frontal gyrus (IFG)--however, impaired semantic control can also follow left temporoparietal lesions, suggesting that this function may be underpinned by a large-scale cortical network. We used repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in healthy volunteers to disrupt processing within 2 potential sites in this network--IFG and posterior middle temporal cortex. Stimulation of both sites selectively disrupted executively demanding semantic judgments: semantic decisions based on strong automatic associations were unaffected. Performance was also unchanged in nonsemantic tasks--irrespective of their executive demands--and following stimulation of a control site. These results reveal that an extended network of prefrontal and posterior temporal regions underpins semantic control.
Figures

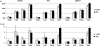
References
-
- Badre D. Cognitive control, hierarchy, and the rostro-caudal organization of the frontal lobes. Trends Cogn Sci. 2008;12:193–200. - PubMed
-
- Badre D, D'Esposito M. Functional magnetic resonance imaging evidence for a hierarchical organization of the prefrontal cortex. J Cogn Neurosci. 2007;19:2082–2099. - PubMed
-
- Badre D, Poldrack RA, Pare-Blagoev EJ, Insler RZ, Wagner AD. Dissociable controlled retrieval and generalized selection mechanisms in ventrolateral prefrontal cortex. Neuron. 2005;47:907–918. - PubMed
-
- Badre D, Wagner AD. Left ventrolateral prefrontal cortex and the cognitive control of memory. Neuropsychologia. 2007;45:2883–2901. - PubMed

