HuMab-7D8, a monoclonal antibody directed against the membrane-proximal small loop epitope of CD20 can effectively eliminate CD20 low expressing tumor cells that resist rituximab-mediated lysis
- PMID: 20851867
- PMCID: PMC2995564
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2010.025783
HuMab-7D8, a monoclonal antibody directed against the membrane-proximal small loop epitope of CD20 can effectively eliminate CD20 low expressing tumor cells that resist rituximab-mediated lysis
Abstract
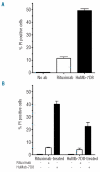
Background: Incorporation of the chimeric CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in the treatment schedule of patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma has significantly improved outcome. Despite this success, about half of the patients do not respond to treatment or suffer from a relapse and additional therapy is required. A low CD20-expression level may in part be responsible for resistance against rituximab. We therefore investigated whether the CD20-expression level related resistance to rituximab could be overcome by a new group of CD20 mAbs (HuMab-7D8 and ofatumumab) targeting a unique membrane-proximal epitope on the CD20 molecule.
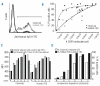
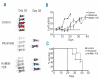
Design and methods: By retroviral transduction of the CD20 gene into CD20-negative cells and clonal selection of transduced cells a system was developed in which the CD20-expression level is the only variable. These CD20 transduced cells were used to study the impact of rituximab and HuMab-7D8 mediated complement-dependent cytotoxicity. To study the in vivo efficacy of these mAbs an in vivo imaging system was generated by retroviral expression of the luciferase gene in the CD20-positive cells.
Results: We show that HuMab-7D8 efficiently killed CD20(low) cells that are not susceptible to rituximab-induced killing in vitro. In a mouse xenograft model, we observed a comparable increase in survival time between HuMab-7D8 and rituximab-treated mice. Most significantly, however, HuMab-7D8 eradicated all CD20-expressing cells both in the periphery as well as in the bone marrow whereas after rituximab treatment CD20(low) cells survived.
Conclusions: Cells that are insensitive to in vitro and in vivo killing by rituximab as the result of their low CD20-expression profile may be efficiently killed by an antibody against the membrane-proximal epitope on CD20. Such antibodies should, therefore, be explored to overcome rituximab resistance in the clinic.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics 2007. Cancer J Clin. 2007;57(1):43–66. - PubMed
-
- Marcus R, Hagenbeek A. The therapeutic use of rituximab in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Eur J Haematol Suppl. 2007:5–14. - PubMed
-
- Groves FD, Linet MS, Travis LB, Devesa SS. Cancer surveillance series: non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma incidence by histologic subtype in the United States from 1978 through 1995. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92(15):1240–51. - PubMed
-
- The Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Classification Project: A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood. 1997;89(11):3909–18. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RI, Gaynor ER, Dahlberg S, Oken MM, Grogan TM, Mize EM, et al. Comparison of a standard regimen (CHOP) with three intensive chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993;328(14):1002–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

