A genetic mouse model of adult-onset, pervasive central nervous system demyelination with robust remyelination
- PMID: 20851998
- PMCID: PMC4415057
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awq247
A genetic mouse model of adult-onset, pervasive central nervous system demyelination with robust remyelination
Abstract
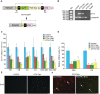
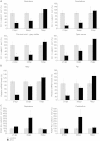
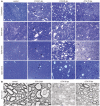
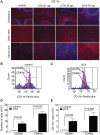
Adult-onset demyelinating disorders of the central nervous system represent the most common neurological abnormalities in young adults. Nevertheless, our understanding of disease pathogenesis and recovery in demyelinating disorders remains incomplete. To facilitate investigation into these processes, we have developed a new mouse model system that allows for the induction of dipththeria toxin A subunit expression in adult oligodendrocytes, resulting in widespread oligodendrocyte loss and demyelination of the central nervous system. These mice develop severe ataxia and tremor that correlates with impaired axonal conduction in the spinal cord. Strikingly, these animals fully recover from their motor and physiological defects and display extensive oligodendrocyte replenishment and widespread remyelination. This model system demonstrates the robust reparative potential of myelin in the central nervous system and provides a promising model for the quantitative assessment of therapeutic interventions that promote remyelination.
Figures


References
-
- Benjamins JA, Morell P. Proteins of myelin and their metabolism. Neurochem Res. 1978;3:137–74. - PubMed
-
- Benjamins JA, Morell P, Hartman BK, Agrawal HC. Central nervous system myelin. In: Lajtha A, editor. Handbook in neurochemistry. New York: Plenum Press; 1984. pp. 361–415.
-
- Blakemore WF, Franklin RJ. Remyelination in experimental models of toxin-induced demyelination. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;318:193–212. - PubMed
-
- Brockschnieder D, Pechmann Y, Sonnenberg-Riethmacher E, Riethmacher D. An improved mouse line for Cre-induced cell ablation due to diphtheria toxin A, expressed from the Rosa26 locus. Genesis. 2006;44:322–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

