The antiretroviral lectin cyanovirin-N targets well-known and novel targets on the surface of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites
- PMID: 20852023
- PMCID: PMC2976296
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00166-10
The antiretroviral lectin cyanovirin-N targets well-known and novel targets on the surface of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites
Abstract
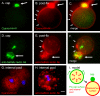
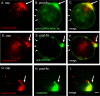
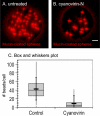
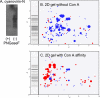
Entamoeba histolytica, the protist that causes amebic dysentery and liver abscess, has a truncated Asn-linked glycan (N-glycan) precursor composed of seven sugars (Man(5)GlcNAc(2)). Here, we show that glycoproteins with unmodified N-glycans are aggregated and capped on the surface of E. histolytica trophozoites by the antiretroviral lectin cyanovirin-N and then replenished from large intracellular pools. Cyanovirin-N cocaps the Gal/GalNAc adherence lectin, as well as glycoproteins containing O-phosphodiester-linked glycans recognized by an anti-proteophosphoglycan monoclonal antibody. Cyanovirin-N inhibits phagocytosis by E. histolytica trophozoites of mucin-coated beads, a surrogate assay for amebic virulence. For technical reasons, we used the plant lectin concanavalin A rather than cyanovirin-N to enrich secreted and membrane proteins for mass spectrometric identification. E. histolytica glycoproteins with occupied N-glycan sites include Gal/GalNAc lectins, proteases, and 17 previously hypothetical proteins. The latter glycoproteins, as well as 50 previously hypothetical proteins enriched by concanavalin A, may be vaccine targets as they are abundant and unique. In summary, the antiretroviral lectin cyanovirin-N binds to well-known and novel targets on the surface of E. histolytica that are rapidly replenished from large intracellular pools.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Entamoeba histolytica: Overexpression of the gal/galnac lectin, ehcp2 and ehcp5 genes in an in vivo model of amebiasis.Parasitol Int. 2016 Dec;65(6 Pt A):665-667. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2016.08.009. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Parasitol Int. 2016. PMID: 27616150
-
Unique Asn-linked oligosaccharides of the human pathogen Entamoeba histolytica.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 27;283(26):18355-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800725200. Epub 2008 Apr 16. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18417475 Free PMC article.
-
Down regulation of Entamoeba histolytica virulence by monoxenic cultivation with Escherichia coli O55 is related to a decrease in expression of the light (35-kilodalton) subunit of the Gal/GalNAc lectin.Infect Immun. 1999 May;67(5):2096-102. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.5.2096-2102.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10225860 Free PMC article.
-
Entamoeba histolytica: from adherence to enteropathy.J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):420-9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.420. J Infect Dis. 1989. PMID: 2536786 Review.
-
Trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica epigenetically silenced in several genes are virulence-attenuated.Parasite. 2008 Sep;15(3):266-74. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2008153266. Parasite. 2008. PMID: 18814693 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of N-glycan precursor length diversity on quality control of protein folding and on protein glycosylation.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 May;41:121-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25475176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asparagine-Linked Glycans of Cryptosporidium parvum Contain a Single Long Arm, Are Barely Processed in the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) or Golgi, and Show a Strong Bias for Sites with Threonine.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017 Apr;16(4 suppl 1):S42-S53. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.066035. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28179475 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of the cyst stage of Entamoeba histolytica.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(5):e1643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001643. Epub 2012 May 8. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012. PMID: 22590659 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams E. W., Ratner D. M., Bokesch H. R., McMahon J. B., O'Keefe B. R., Seeberger P. H. 2004. Oligosaccharide and glycoprotein microarrays as tools in HIV glycobiology; glycan-dependent gp120/protein interactions. Chem. Biol. 11:875–881 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

