Development of sarcoidosis following completion of treatment for hepatitis C with pegylated interferon-{alpha}2a and ribavirin: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 20852086
- PMCID: PMC3006563
- DOI: 10.3121/cmr.2010.886
Development of sarcoidosis following completion of treatment for hepatitis C with pegylated interferon-{alpha}2a and ribavirin: a case report and literature review
Abstract
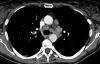
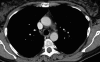
Sarcoidosis is a chronic inflammatory multisystem disease of unknown etiology. We report on a woman, aged 57 years, presenting with typical sarcoidosis occurring two months after completion of a six-month course of interferon-α and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. The current observation is interesting with regard to the time elapsed between the occurrence of symptoms and antiviral treatment withdrawal, and spontaneous recovery after ten months of follow-up. Pathophysiological mechanisms involved in the development of antiviral therapy-induced sarcoidosis are discussed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Development of sarcoidosis during treatment for chronic hepatitis C with pegylated interferon alfa-2a and ribavirin: case report and literature review].Infez Med. 2013 Mar;21(1):40-44. Infez Med. 2013. PMID: 23524900 Review. Italian.
-
[Cutaneous sarcoidosis after treatment with interferon for hepatitis C: A not entirely rare but often overlooked reaction].Pathologe. 2016 Mar;37(2):184-6. doi: 10.1007/s00292-015-0127-7. Pathologe. 2016. PMID: 26769217 German.
-
[Cutaneous sarcoidosis during pegylated interferon alpha and ribavirin treatment of chronic hepatitis C--a case report].Cesk Patol. 2007 Jan;43(1):27-30. Cesk Patol. 2007. PMID: 17370474 Czech.
-
Interferon-induced sarcoidosis.BMJ Case Rep. 2011 Apr 19;2011:bcr0320113929. doi: 10.1136/bcr.03.2011.3929. BMJ Case Rep. 2011. PMID: 22696628 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous sarcoidosis developing after treatment with pegylated interferon and ribavirin: a new case and review of the literature.Int J Dermatol. 2011 Mar;50(3):287-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04728.x. Int J Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21342161 Review.
Cited by
-
Sarcoidosis and chronic hepatitis C: treatment with prednisone and colchicine.An Bras Dermatol. 2016 Apr;91(2):231-4. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164029. An Bras Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27192527 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon α-induced sarcoidosis to a patient with polycythemia vera.BMJ Case Rep. 2011 May 10;2011:bcr0120113740. doi: 10.1136/bcr.01.2011.3740. BMJ Case Rep. 2011. PMID: 22696707 Free PMC article.
-
A case of capecitabine-induced sarcoidosis.Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2012 Mar;72(3):318-22. doi: 10.4046/trd.2012.72.3.318. Epub 2012 Mar 31. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2012. PMID: 23227072 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-alpha-induced sarcoidosis in a patient being treated for hepatitis C.Am J Case Rep. 2014 May 28;15:235-8. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.890180. eCollection 2014. Am J Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 24900166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Costalbel U, Hunninghake GW. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Statement Committee. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society. World Association for Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders. Eur Respir J 1999;14:735–737. - PubMed
-
- Hunninghake GW, Costabel U, Ando M, Baughman R, Cordier JF, du Bois R, Eklund A, Kitaichi M, Lynch J, Rizzato G, Rose C, Selroos O, Semenzato G, Sharma OP. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society. World Association for Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 1999;16:149–173. - PubMed
-
- Davis GL, Balart LA, Schiff ER, Lindsay K, Bodenheimer HC Jr, Perrillo RP, Carey W, Jacobson IM, Payne J, Dienstag JL, et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C with recombinant interferon alpha. A multicenter randomized, controlled trial. Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N Engl J Med 1989;321:1501–1506. - PubMed
-
- Leclerc S, Myers RP, Moussalli J, Herson S, Poynard T, Benveniste O. Sarcoidosis and interferon therapy: report of five cases and review of the literature. Eur J Intern Med 2003;14:237–243. - PubMed
-
- Ravanel JG, McAdams HP, Plankeel JF, Butnor KJ, Sporn TA. Sarcoidosis induced by interferon therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001;177:199–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
