MatrixDB, the extracellular matrix interaction database
- PMID: 20852260
- PMCID: PMC3013758
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq830
MatrixDB, the extracellular matrix interaction database
Abstract
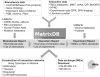
MatrixDB (http://matrixdb.ibcp.fr) is a freely available database focused on interactions established by extracellular proteins and polysaccharides. Only few databases report protein-polysaccharide interactions and, to the best of our knowledge, there is no other database of extracellular interactions. MatrixDB takes into account the multimeric nature of several extracellular protein families for the curation of interactions, and reports interactions with individual polypeptide chains or with multimers, considered as permanent complexes, when appropriate. MatrixDB is a member of the International Molecular Exchange consortium (IMEx) and has adopted the PSI-MI standards for the curation and the exchange of interaction data. MatrixDB stores experimental data from our laboratory, data from literature curation, data imported from IMEx databases, and data from the Human Protein Reference Database. MatrixDB is focused on mammalian interactions, but aims to integrate interaction datasets of model organisms when available. MatrixDB provides direct links to databases recapitulating mutations in genes encoding extracellular proteins, to UniGene and to the Human Protein Atlas that shows expression and localization of proteins in a large variety of normal human tissues and cells. MatrixDB allows researchers to perform customized queries and to build tissue- and disease-specific interaction networks that can be visualized and analyzed with Cytoscape or Medusa.
Figures

References
-
- Ricard-Blum S, Ruggiero F. The collagen superfamily: from the extracellular matrix to the cell membrane. Pathol. Biol. (Paris) 2005;53:430–442. - PubMed
-
- Ricard-Blum S, Ballut L. Matricryptins derived from collagens and proteoglycans. Front Biosci. in press. - PubMed
-
- Bateman JF, Boot-Handford RP, Lamandé SR. Genetic diseases of connective tissues: cellular and extracellular effects of ECM mutations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009;10:173–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

