Escherichia coli RecBC helicase has two translocase activities controlled by a single ATPase motor
- PMID: 20852646
- PMCID: PMC2950890
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1901
Escherichia coli RecBC helicase has two translocase activities controlled by a single ATPase motor
Abstract
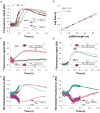
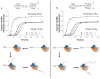
E. coli RecBCD is a DNA helicase with two ATPase motors (RecB, a 3'→5' translocase, and RecD, a 5'→3' translocase) that function in repair of double-stranded DNA breaks. The RecBC heterodimer, with only the RecB motor, remains a processive helicase. Here we examined RecBC translocation along single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). Notably, we found RecBC to have two translocase activities: the primary translocase moves 3'→5', whereas the secondary translocase moves RecBC along the opposite strand of a forked DNA at a similar rate. The secondary translocase is insensitive to the ssDNA backbone polarity, and we propose that it may fuel RecBCD translocation along double-stranded DNA ahead of the unwinding fork and ensure that the unwound single strands move through RecBCD at the same rate after interaction with a crossover hot-spot indicator (Chi) sequence.
Figures
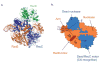
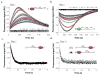
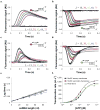
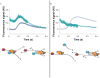
Comment in
-
One motor driving two translocases.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Oct;17(10):1166-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1010-1166. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20924403
References
-
- Singleton MR, Dillingham MS, Wigley DB. Structure and Mechanism of Helicases and Nucleic Acid Translocases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:23–50. - PubMed
-
- Dillingham MS, Spies M, Kowalczykowski SC. RecBCD enzyme is a bipolar DNA helicase. Nature. 2003;423:893–897. - PubMed
-
- Taylor AF, Smith GR. RecBCD enzyme is a DNA helicase with fast and slow motors of opposite polarity. Nature. 2003;423:889–893. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

