Muscarinic receptor antagonist and an alpha-adrenergic agonist are required in combination to provide stable mydriasis following intravitreal injection in mice
- PMID: 20852745
- PMCID: PMC2941443
Muscarinic receptor antagonist and an alpha-adrenergic agonist are required in combination to provide stable mydriasis following intravitreal injection in mice
Abstract
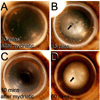
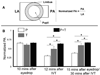
Tropicamide (muscarinic receptor antagonist) and phenylephrine (α-adrenergic receptor agonist) are commonly used to dilate the pupils by topical application. These two eye drops are often used, singly or in combination, to dilate the pupil and perform acute light-evoked physiological experiments (electroretinography, for example), before and after intravitreal injections of pharmacological agents, as an assay for their affect on retinal activity. This study wanted to determine whether treatment with one of these drugs, or with both, is most effective in maintaining mydriasis after intravitreal injections. Changes in pupillary dilation before and after intravitreal injection of balanced salt solution (0.5 µl) were recorded. Phenylephrine (α-adrenergic agonist) and tropicamide (muscarinic agonist) when combined, but not singly, produced full and stable pupillary dilation following intravitreal injections. Re-instillation of topical mydriatics after intravitreal injections was required for maximal pupillary dilation. A combination of a muscarinic receptor antagonist and an alpha-adrenergic agonist is required for stable mydriasis following intravitreal injection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Topical mydriatics affect light-evoked retinal responses in anesthetized mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Jan;51(1):567-76. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4168. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19661232 Free PMC article.
-
[Same-eye comparison of pupillary dilation with an intraoperative standardized intracameral combination of mydriatics (Mydrane®) versus a preoperative ophthalmic (Mydriasert®) in standard cataract surgery in non-diabetic patients (French translation of the article)].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019 Dec;42(10):1068-1077. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2019.02.015. Epub 2019 Oct 23. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019. PMID: 31668379 Clinical Trial. French.
-
Effects of Mydriatics on Rod/Cone- and Melanopsin-driven Pupil Responses.Optom Vis Sci. 2020 Mar;97(3):198-206. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001486. Optom Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32168243 Free PMC article.
-
Dapiprazole: will it affect the standard of care for pupillary dilation?Optom Clin. 1992;2(4):113-20. Optom Clin. 1992. PMID: 1363078 Review.
-
Pharmacologic interventions for mydriasis in cataract surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 27;5(5):CD012830. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012830.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34043237 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pupil to limbus ratio: Introducing a simple objective measure using two-box method for measuring early anisocoria and progress of pupillary change in the ICU.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2015 Apr-Jun;6(2):208-15. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.153229. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2015. PMID: 25883482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Backstrom G, Behndig A. Redilatation with intracameral mydriatics in phacoemulsification surgery. Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica. 2006;84(1):100–104. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett JD, Jaanus SD. Clinical ocular pharmacology. Butterworth-Heinemann; 2008.
-
- Federman JL, Anand R. Surgical dilation of the pupil during pars plana vitrectomy. Ophthalmic Surgery. 1989;20(1):46–48. - PubMed
-
- Fulton AB, Rushton WA. The human rod ERG: correlation with psychophysical responses in light and dark adaptation. Vision Research. 1978;18(7):793–800. - PubMed
-
- Fulton AB, Hansen RM. Scotopic stimulus/response relations of the B-wave of the electroretinogram. Documenta Ophthalmologica. 1988;68(3–4):293–304. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
