Efficient strategy for controlling postoperative hemorrhage in total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 20852844
- PMCID: PMC3096774
- DOI: 10.1007/s00167-010-1263-5
Efficient strategy for controlling postoperative hemorrhage in total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of the present study was to compare the intraoperative use of tranexamic acid (TNA) plus intra-articular diluted-epinephrine (DEP) with preoperative autologous blood donations and transfusions in reducing an allogeneic blood transfusion (ABT) in primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
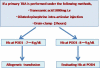
Methods: Patients (n=133) treated with unilateral primary TKA were divided into three groups retrospectively: patients administered autologous blood transfusions were assigned to group A (n=51); patients administered preoperative injections of TNA and postoperative intra-articular injections of DEP were assigned to group B (n=42); and patients treated with the drain-clamp method in addition to injections of TNA and DEP were assigned to group C (n=40). The rate of avoidance of ABTs, postoperative blood loss, and complications (DVT/PE, skin problems) were examined.
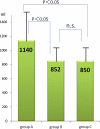
Results: The differences among the three groups were not significant in terms of the proportion of patients requiring no ABTs (94% in group A, 93% in group B and 95% in group C, n.s.). The total blood loss calculated was 1,140±451 ml, 852±343 ml, and 850±296 ml, respectively (group B>A, group C>A, P=0.0009). The significant complications were not observed in three groups.
Conclusion: The results of the study showed that the TNA plus DEP combination exerted a comparable effect with preoperative autologous blood transfusion in avoiding ABTs in unilateral primary TKA. Considering several problems of preoperative autologous blood donation, the use of TNA plus DEP is recommended. In addition, it is highly possible that allogeneic blood transfusions can be avoided for patients with preoperative Hb values≥10.5 using the method described in this study, and the need for preoperative autologous blood donations can be decreased.
Figures
References
-
- Benoni G, Fredin H. Fibrinolytic inhibition with tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and blood transfusion after knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomised, double-blind study of 86 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78:434–440. - PubMed
-
- Bierbaum BE, Callaghan JJ, Galante JO, Rubash HE, Tooms RE, Welch RB. An analysis of blood management in patients having a total hip or knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81:2–10. - PubMed
-
- Billote DB, Glisson SN, Green D, Wixson RL. A prospective, randomized study of preoperative autologous donation for hip replacement surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84:1299–1304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous