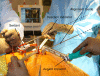
Improving cup positioning using a mechanical navigation instrument
- PMID: 20852974
- PMCID: PMC3018200
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-010-1553-8
Improving cup positioning using a mechanical navigation instrument
Abstract
Background: Although surgical navigation reduces the rate of malpositioned acetabular cups in total hip arthroplasty (THA), its use has not been widely adopted. As a result of our perceived need for simple and efficient methods of navigation, we developed a mechanical navigation device for acetabular cup orientation.
Questions/purposes: We assessed accuracy of cup orientation (mean error of cup inclination and anteversion) of a novel mechanical navigation device, percentage of outliers, length of operation, and compared the results with a series of CT-based computer-assisted THAs.
Methods: Cup orientation of 70 THAs performed using the mechanical navigation device was compared with a historical control group of 146 THAs performed using CT-based computer navigation. Postoperative cup orientation was measured using a validated two-dimensional/three-dimensional matching method. An outlier was defined outside a range of ± 10° from the planned inclination and/or anteversion.
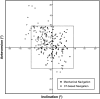
Results: Using the mechanical navigation device, we observed a decrease in the errors of inclination (1.3° ± 3.4° [range, -6.6° to 8.2°] versus 3.5° ± 4.2° [-12.7° to 6.9°]), errors of anteversion (1.0° ± 4.1° [-8.8° to 9.5°] versus 3.0° ± 5.8° [-11.8° to 19.6°]), percentages of outliers (0% versus 9.6%), and length of operation (112 ± 22 [78-184] minutes versus 132 ± 18 [90-197] minutes) compared with CT-based navigation.
Conclusions: Compared with CT-based surgical navigation, navigation of acetabular cup orientation using a mechanical device can be performed in less time, lower mean errors, and minimal equipment.
Figures


References
-
- Dorr LD. Hip Arthroplasty: Minimally Invasive Techniques and Computer Navigation. 1. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders; 2005.
-
- Hube R, Birke A, Hein W, Klima S. CT-based and fluoroscopy-based navigation for cup implantation in total hip arthroplasty (THA) Surg Technol Int. 2003;11:275–280. - PubMed

