NF-κB/Rel proteins and the humoral immune responses of Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 20852987
- PMCID: PMC3083852
- DOI: 10.1007/82_2010_107
NF-κB/Rel proteins and the humoral immune responses of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
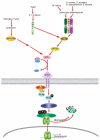
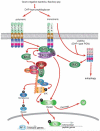
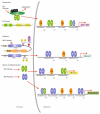
Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB)/Rel transcription factors form an integral part of innate immune defenses and are conserved throughout the animal kingdom. Studying the function, mechanism of activation and regulation of these factors is crucial for understanding host responses to microbial infections. The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster has proved to be a valuable model system to study these evolutionarily conserved NF-κB mediated immune responses. Drosophila combats pathogens through humoral and cellular immune responses. These humoral responses are well characterized and are marked by the robust production of a battery of anti-microbial peptides. Two NF-κB signaling pathways, the Toll and the IMD pathways, are responsible for the induction of these antimicrobial peptides. Signal transduction in these pathways is strikingly similar to that in mammalian TLR pathways. In this chapter, we discuss in detail the molecular mechanisms of microbial recognition, signal transduction and NF-κB regulation, in both the Toll and the IMD pathways. Similarities and differences relative to their mammalian counterparts are discussed, and recent advances in our understanding of the intricate regulatory networks in these NF-κB signaling pathways are also highlighted.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

