Functional characterization of stem cell activity in the mouse mammary gland
- PMID: 20853073
- PMCID: PMC3492888
- DOI: 10.1007/s12015-010-9191-9
Functional characterization of stem cell activity in the mouse mammary gland
Abstract
Any portion of the mouse mammary gland is capable of recapitulating a clonally derived complete and functional mammary tree upon transplantation into an epithelial divested mammary fat-pad of a recipient host. As such, it is an ideal model tissue for the study somatic stem cell function. This review will outline what is known regarding the function of stem/progenitor cells in the mouse mammary gland, including how progenitor populations can be functionally defined, the evidence for and potential role of selective DNA strand segregation, and the role of the niche in maintaining and controlling stem cell function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
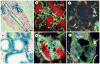
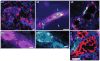
References
-
- Deome K, Faulkin LJ, Bern H, Blair P. Development of mammary tumors from hyperplastic alveolar nodules transplanted into gland-free mammary fat pads of female C3H mice. Cancer Research. 1959;19:515–520. - PubMed
-
- Faulkin LJ, Jr, Deome KB. Regulation of growth and spacing of gland elements in the mammary fat pad of the C3H mouse. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1960;24:953–969. - PubMed
-
- Daniel CW, Deome KB. Growth of mouse mammary glands in vivo after monolayer culture. Science. 1965;149:634–636. - PubMed
-
- Daniel CW, Aidells BD, Medina D, Faulkin LJ., Jr Unlimited division potential of precancerous mouse mammary cells after spontaneous or carcinogen-induced transformation. Federation Proceedings. 1975;34:64–67. - PubMed
-
- Smith GH, Medina D. A morphologically distinct candidate for an epithelial stem cell in mouse mammary gland. Journal of Cell Science. 1988;90(Pt 1):173–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

