A novel strategy for development of glucocorticoids through non-genomic mechanism
- PMID: 20853130
- PMCID: PMC11114530
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0526-0
A novel strategy for development of glucocorticoids through non-genomic mechanism
Abstract
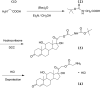
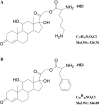
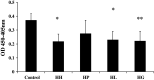
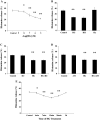
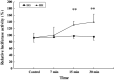
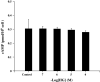
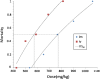
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are routinely believed to take effect through genomic mechanisms, which are also largely responsible for GCs' side effects. Beneficial non-genomic effects of GCs have been reported as being independent of the genomic pathway. Here, we synthesized a new type of GCs, which took effect mainly via non-genomic mechanisms. Hydrocortisone was conjugated with glycine, lysine and phenylalanine to get a bigger molecular structure, which could hardly go through the cell membrane. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory efficacy showed that hydrocortisone-conjugated glycine (HG) and lysine could inhibit neutrophil degranulation within 15 min. HG could inhibit IgE-mediated histamine release from mast cells via a non-genomic pathway, and rapidly alleviate allergic reaction. Luciferase reporter assay showed that HG would not activate the glucocorticoid response element within 30 min, which verified the rapid effects independent of the genomic pathway. The work proposes a novel insight into the development of novel GCs, and provides new tools for experimental study on non-genomic mechanisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoids inhibit degranulation of mast cells in allergic asthma via nongenomic mechanism.Allergy. 2008 Sep;63(9):1177-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01725.x. Allergy. 2008. PMID: 18699934
-
Rapid non-genomic inhibitory effects of glucocorticoids on human neutrophil degranulation.Inflamm Res. 2005 Jan;54(1):37-41. doi: 10.1007/s00011-004-1320-y. Inflamm Res. 2005. PMID: 15723203
-
The novel strategy of glucocorticoid drug development via targeting nongenomic mechanisms.Steroids. 2015 Oct;102:27-31. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2015.06.015. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Steroids. 2015. PMID: 26122209 Review.
-
Rapid inhibitory effect of corticosterone on histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells.Horm Metab Res. 2007 Apr;39(4):273-7. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-973809. Horm Metab Res. 2007. PMID: 17447165
-
Neutrophil recruitment in mast cell-dependent inflammation: inhibitory mechanisms of glucocorticoids.Inflamm Res. 2004 Dec;53(12):644-52. doi: 10.1007/s00011-004-1307-8. Inflamm Res. 2004. PMID: 15654511 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic and non-genomic effects of glucocorticoids: implications for breast cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jan 1;8(1):1-10. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25755688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Glucocorticoids in Breast Cancer Therapy.Curr Oncol. 2022 Dec 25;30(1):298-314. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30010024. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36661673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoids Regulate the Vascular Remodeling of Aortic Dissection Via the p38 MAPK-HSP27 Pathway Mediated by Soluble TNF-RII.EBioMedicine. 2018 Jan;27:247-257. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.12.002. Epub 2017 Dec 6. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 29287621 Free PMC article.
-
Non-genomic effect of glucocorticoids on cardiovascular system.Pflugers Arch. 2012 Dec;464(6):549-59. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1155-2. Epub 2012 Sep 23. Pflugers Arch. 2012. PMID: 23001133 Review.
-
Non-genomic inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids on activated peripheral blood basophils through suppression of lipid raft formation.Clin Exp Immunol. 2012 Oct;170(1):86-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04636.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22943204 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

