A 10-year follow-up of treatment outcomes in patients with early stage breast cancer and clinically negative axillary nodes treated with tangential breast irradiation following sentinel lymph node dissection or axillary clearance
- PMID: 20853176
- PMCID: PMC3623372
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-010-1167-6
A 10-year follow-up of treatment outcomes in patients with early stage breast cancer and clinically negative axillary nodes treated with tangential breast irradiation following sentinel lymph node dissection or axillary clearance
Abstract
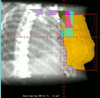
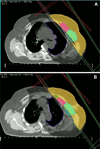
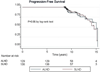
We compare long-term outcomes in patients with node negative early stage breast cancer treated with breast radiotherapy (RT) without the axillary RT field after sentinel lymph node dissection (SLND) or axillary lymph node dissection (ALND). We hypothesize that though tangential RT was delivered to the breast tissue, it at least partially sterilized occult axillary nodal metastases thus providing low nodal failure rates. Between 1995 and 2001, 265 patients with AJCC stages I-II breast cancer were treated with lumpectomy and either SLND (cohort SLND) or SLND and ALND (cohort ALND). Median follow-up was 9.9 years (range 8.3-15.3 years). RT was administered to the whole breast to the median dose of 48.2 Gy (range 46.0-50.4 Gy) plus boost without axillary RT. Chi-square tests were employed in comparing outcomes of two groups for axillary and supraclavicular failure rates, ipsilateral in-breast tumor recurrence (IBTR), distant metastases (DM), and chronic complications. Progression-free survival (PFS) was compared using log-rank test. There were 136/265 (51%) and 129/265 (49%) patients in the SLND and ALND cohorts, respectively. The median number of axillary lymph nodes assessed was 2 (range 1-5) in cohort SLND and 18 (range 7-36) in cohort ALND (P < 0.0001). Incidence of AFR and SFR in both cohorts was 0%. The rates of IBTR and DM in both cohorts were not significantly different. Median PFS in the SLND cohort is 14.6 years and 10-year PFS is 88.2%. Median PFS in the ALND group is 15.0 years and 10-year PFS is 85.7%. At a 10-year follow-up chronic lymphedema occurred in 5/108 (4.6%) and 40/115 (34.8%) in cohorts SLND and ALND, respectively (P = 0.0001). This study provides mature evidence that patients with negative nodes, treated with tangential breast RT and SLND alone, experience low AFR or SFR. Our findings, while awaiting mature long-term data from NSABP B-32, support that in patients with negative axillary nodal status such treatment provides excellent long-term cure rates while avoiding morbidities associated with ALND or addition of axillary RT field.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complication rates in patients with negative axillary nodes 10 years after local breast radiotherapy after either sentinel lymph node dissection or axillary clearance.Am J Clin Oncol. 2013 Feb;36(1):12-9. doi: 10.1097/COC.0b013e3182354bda. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 22134519 Free PMC article.
-
Axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection in women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: a randomized clinical trial.JAMA. 2011 Feb 9;305(6):569-75. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.90. JAMA. 2011. PMID: 21304082 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Axillary Dissection vs No Axillary Dissection on 10-Year Overall Survival Among Women With Invasive Breast Cancer and Sentinel Node Metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2017 Sep 12;318(10):918-926. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.11470. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28898379 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Improved axillary staging of breast cancer with sentinel lymphadenectomy.Ann Surg. 1995 Sep;222(3):394-9; discussion 399-401. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199509000-00016. Ann Surg. 1995. PMID: 7677468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staging of women with breast cancer after introduction of sentinel node guided axillary dissection.Dan Med J. 2012 Jul;59(7):B4475. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 22759850 Review.
Cited by
-
Immediate Implant Reconstruction Is Associated With a Reduced Risk of Lymphedema Compared to Mastectomy Alone: A Prospective Cohort Study.Ann Surg. 2016 Feb;263(2):399-405. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001128. Ann Surg. 2016. PMID: 25607768 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema (BCRL) and Bioimpedance Spectroscopy: Long-Term Follow-Up, Surveillance Recommendations, and Multidisciplinary Risk Factors.Ann Surg Oncol. 2023 Oct;30(10):6258-6265. doi: 10.1245/s10434-023-13956-9. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37535267
-
Manual Lymphatic Drainage after Subepidermal Tracer Injection Optimizes Results of Sentinel Lymph Node Labeling in Primary Breast Cancer.Breast Care (Basel). 2016 Feb;11(1):40-4. doi: 10.1159/000442727. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Breast Care (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27051395 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized study to prevent lymphedema in women treated for breast cancer: CALGB 70305 (Alliance).Cancer. 2021 Jan 15;127(2):291-299. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33183. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33079411 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Risk of lymphedema after mastectomy: potential benefit of applying ACOSOG Z0011 protocol to mastectomy patients.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014 Feb;144(1):71-7. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-2856-3. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014. PMID: 24500108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fisher B, Jeong JH, Anderson S, Bryant J, Fisher ER, Wolmark N. Twenty-five-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing radical mastectomy, total mastectomy, and total mastectomy followed by irradiation. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(8):567–575. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, Margolese RG, Deutsch M, Fisher ER, Jeong JH, Wolmark N. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(16):1233–1241. - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Galimberti V, Paganelli G, Maisonneuve P, Viale G, Orecchia R, Luini A, Intra M, Veronesi P, Caldarella P, Renne G, Rotmensz N, Sangalli C, De Brito Lima L, Tullii M, Zurrida S. Axillary metastases in breast cancer patients with negative sentinel nodes: a follow-up of 3548 cases. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45(8):1381–1388. - PubMed
-
- Larson D, Weinstein M, Goldberg I, Silver B, Recht A, Cady B, Silen W, Harris JR. Edema of the arm as a function of the extent of the axillary surgery inpatients with Stage I-II carcinoma of the breast treated with primary radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986;12:1575–1583. - PubMed
-
- Mansel RE, Fallowfield L, Kissin M, Goyal A, Newcombe RG, Dixon JM, Yiangou C, Horgan K, Bundred N, Monypenny I, England D, Sibbering M, Abdullah TI, Barr L, Chetty U, Sinnett DH, Fleissig A, Clarke D, Ell PJ. Randomized multicenter trial of sentinel node biopsy versus standard axillary treatment in operable breast cancer: The ALMANAC Trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:599–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

