Clinical outcomes of an integrated treatment for depression and substance use disorders
- PMID: 20853931
- PMCID: PMC3609717
- DOI: 10.1037/a0019943
Clinical outcomes of an integrated treatment for depression and substance use disorders
Abstract
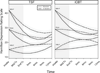
The authors compared longitudinal treatment outcomes for depressed substance-dependent veterans (N = 206) assigned to integrated cognitive-behavioral therapy plus standard pharmacotherapy (ICBT + P) or 12-step facilitation therapy plus standard pharmacotherapy (TSF + P). Drug and alcohol involvement and depressive symptomology were measured at intake and at 3-month intervals during treatment and up to 1 year posttreatment. Participants in both treatment conditions showed decreased depression and substance use from intake. ICBT + P participants maintained improvements in substance involvement over time, whereas TSF + P participants had more rapid increases in use in the months following treatment. Decreases in depressive symptoms were more pronounced for TSF + P than ICBT + P in the 6 months posttreatment. Within both treatment groups, higher attendance was associated with improved substance use and depression outcomes over time. Initial levels of depressive symptomology had a complex predictive relationship with long-term depression outcomes. Early treatment response predicted long-term substance use outcomes for a portion of the sample. Although both treatments were associated with improvements in substance use and depression, ICBT + P may lead to more stable substance use reductions compared with TSF + P.
Figures



References
-
- Alterman AI, Brown LS, Zaballero A, McKay JR. Interviewer severity ratings and composite scores of the ASI– a further look. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 1994;34:201–209. - PubMed
-
- Blume AW, Schmaling KB, Marlatt GA. Revisiting the self-medication hypothesis from a behavioral perspective. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice. 2000;7:379–384.
-
- Brown SA, D’Amico EJ. Outcomes for alcohol treatment for adolescents. In: Galanter M, editor. Recent developments on alcoholism: Vol. XVI. Selected treatment topics. New York: Plenum; 2001. pp. 307–327. - PubMed
-
- Brown SA, Glasner-Edwards SV, Tate SR, McQuaid JR, Chalekian MS, Granholm E. Integrated cognitive behavioral therapy versus twelve-step facilitation therapy for substance dependent adults with depressive disorders. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 2006;38:449–460. - PubMed

