Docosahexaenoic acid prevents dendritic cell maturation, inhibits antigen-specific Th1/Th17 differentiation and suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 20854895
- PMCID: PMC3031664
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.09.012
Docosahexaenoic acid prevents dendritic cell maturation, inhibits antigen-specific Th1/Th17 differentiation and suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
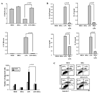
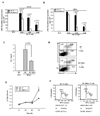
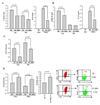
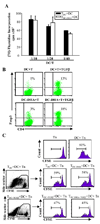
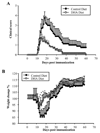
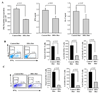
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), the most abundant essential n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid in the CNS, emerged recently together with eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and DHA/EPA metabolic derivatives as a major player in the resolution of inflammation. Protective anti-inflammatory effects of DHA were reported in clinical studies and animal models of colitis, sepsis, and stroke. Here we report for the first time a beneficial effect of dietary n-3 fatty acids in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a model for human multiple sclerosis. In the present study we investigated the effects of DHA on the function of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (DC) in CD4(+) T cell stimulation and differentiation. Pretreatment of DC with DHA prevented LPS-induced DC maturation, maintaining an immature phenotype characterized by low expression of costimulatory molecules and lack of proinflammatory cytokine production (IL-12p70, IL-6, and IL-23). DHA-treated DC were poor stimulators of antigen-specific T cells in terms of proliferation and Th1/Th17 differentiation. This was associated with an increase in p27(kip1), a cell cycle arresting agent, and with decreases in Tbet, GATA-3, and RORγt, master transcription factors for Th1, Th2, and Th17. In contrast, T cells co-cultured with DC-DHA express higher levels of TGFβ and Foxp3, without exhibiting a functional Treg phenotype. Similar to the in vitro results, the beneficial effect of DHA in EAE was associated with reduced numbers of IFNγ- and IL-17-producing CD4(+) T cells in both spleen and CNS.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Docosahexaenoic acid prevents dendritic cell maturation and in vitro and in vivo expression of the IL-12 cytokine family.Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Feb 1;9:12. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-12. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20122166 Free PMC article.
-
Mannan-conjugated myelin peptides prime non-pathogenic Th1 and Th17 cells and ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Exp Neurol. 2015 May;267:254-67. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.10.019. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25447934
-
Amlexanox attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting dendritic cell maturation and reprogramming effector and regulatory T cell responses.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Mar 1;16(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1438-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 30823934 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of CNS inflammatory demyelination.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Oct 15;333(1-2):76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23578791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green tea EGCG, T cells, and T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases.Mol Aspects Med. 2012 Feb;33(1):107-18. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2011.10.001. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Mol Aspects Med. 2012. PMID: 22020144 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential sufficiency of zinc, ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamin D and magnesium for prevention and treatment of COVID-19, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, lung diseases and cancer.Biochimie. 2021 Aug;187:94-109. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2021.05.013. Epub 2021 May 31. Biochimie. 2021. PMID: 34082041 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Transcription Factors in the Management of Preterm Birth: Impact on Future Treatment Strategies.Reprod Sci. 2023 May;30(5):1408-1420. doi: 10.1007/s43032-022-01087-7. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 36131222 Review.
-
Dendritic cell activation, phagocytosis and CD69 expression on cognate T cells are suppressed by n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids.Immunology. 2013 Jul;139(3):386-94. doi: 10.1111/imm.12088. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23373457 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally Occurring Nervonic Acid Ester Improves Myelin Synthesis by Human Oligodendrocytes.Cells. 2019 Jul 29;8(8):786. doi: 10.3390/cells8080786. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31362382 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid desaturation by stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 controls regulatory T cell differentiation and autoimmunity.Cell Mol Immunol. 2023 Jun;20(6):666-679. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01011-2. Epub 2023 Apr 12. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37041314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arita M, Yoshida M, Hong S, Tjonahen E, Glickman JN, Petasis NA, Blumberg RS, Serhan CN. Resolvin E1, an endogenous lipid mediator derived from omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid, protects against 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:7671–7676. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Attakpa E, Hichami A, Simonin AM, Sanson EG, Dramane KL, Khan NA. Docosahexaenoic acid modulates the expression of T-bet and GATA-3 transcription factors, independently of PPARalpha, through suppression of MAP kinase activation. Biochimie. 2009;91:1359–1365. - PubMed
-
- Bailes JE, Mills JD. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) Reduces Traumatic Axonal Injury in a Rodent Head Injury Model. J Neurotrauma. 2010 - PubMed
-
- Bailey SL, Schreiner B, McMahon EJ, Miller SD. CNS myeloid DCs presenting endogenous myelin peptides ‘preferentially’ polarize CD4+ T(H)−17 cells in relapsing EAE. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:172–180. - PubMed
-
- Bannenberg GL. Resolvins: Current understanding and future potential in the control of inflammation. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2009;12:644–658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

