N-terminal truncation of Stat5a/b circumvents PIAS3-mediated transcriptional inhibition of Stat5 in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 20854925
- PMCID: PMC2982800
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.09.008
N-terminal truncation of Stat5a/b circumvents PIAS3-mediated transcriptional inhibition of Stat5 in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
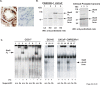
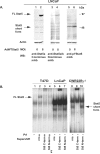
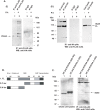
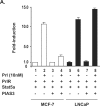
Transcription factor Stat5a/b is critical for prostate cancer cell survival and for prostate xenograft tumor growth. In addition, the Stat5a/b signaling pathway may contribute to progression of organ-confined prostate cancer to castration-resistant and/or metastatic disease. Expression of nuclear Stat5a/b is clustered to high grade human prostate cancers, and nuclear Stat5a/b in primary prostate cancer predicts early disease recurrence after initial treatment. Here, we show by Western blotting and electromobility shift assay that Stat5a/b protein in human prostate cancer is N-terminally truncated. This short form of Stat5a/b is generated post-translationally in vivo in prostate cancer cells and is the predominant form of Stat5a/b that binds to DNA. We further demonstrate by mutagenesis and co-immunoprecipitations that the N-domain of Stat5a/b is required for binding to PIAS3, and that PIAS3 inhibits transcriptional activity of Stat5a/b in breast cancer cells but not in prostate cancer cells. Thus, the proteolytic cleavage of the N-terminus of Stat5a/b may be a mechanism by which Stat5 evades the transcriptional repression by PIAS3 in prostate cancer cells, and results in increased Stat5-driven gene expression and prostate cancer progression.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 promotes growth of human prostate cancer cells in vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Mar 1;14(5):1317-24. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-2024. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18316550
-
Pharmacologic inhibition of Jak2-Stat5 signaling By Jak2 inhibitor AZD1480 potently suppresses growth of both primary and castrate-resistant prostate cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Oct 15;19(20):5658-74. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0422. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23942095 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Based Screen Identifies a Potent Small Molecule Inhibitor of Stat5a/b with Therapeutic Potential for Prostate Cancer and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Aug;14(8):1777-93. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0883. Epub 2015 May 29. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26026053 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5a/b: biomarker and therapeutic target in prostate and breast cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Oct;43(10):1417-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.06.007. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21704724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A/B in prostate and breast cancers.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008 Jun;15(2):367-90. doi: 10.1677/ERC-08-0013. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18508994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Stat5a/b Enhances Proteasomal Degradation of Androgen Receptor Liganded by Antiandrogens in Prostate Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Mar;14(3):713-26. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0819. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 25552366 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis revealed a correlation of PIAS family genes expression with prognosis, immunomodulation and chemotherapy.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Mar 25;29(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01795-7. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38528630 Free PMC article.
-
GTN Enhances Antitumor Effects of Doxorubicin in TNBC by Targeting the Immunosuppressive Activity of PMN-MDSC.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;15(12):3129. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123129. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370739 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen receptor-dependent and -independent mechanisms driving prostate cancer progression: Opportunities for therapeutic targeting from multiple angles.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3724-3745. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12554. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27741508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Selected STAT Inhibitors with Prolactin-Induced Protein (PIP) in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 7;26(4):1416. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041416. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahonen TJ, Harkonen PL, Rui H, Nevalainen MT. PRL signal transduction in the epithelial compartment of rat prostate maintained as long-term organ cultures in vitro. Endocrinology. 2002;143:228–38. - PubMed
-
- Ahonen TJ, Xie J, LeBaron MJ, Zhu J, Nurmi M, Alanen K, et al. Inhibition of transcription factor Stat5 induces cell death of human prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:27287–92. - PubMed
-
- Assikis VJ, Do KA, Wen S, Wang X, Cho-Vega JH, Brisbay S, et al. Clinical and biomarker correlates of androgen-independent, locally aggressive prostate cancer with limited metastatic potential. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:6770–8. - PubMed
-
- Azam M, Lee C, Strehlow I, Schindler C. Functionally distinct isoforms of STAT5 are generated by protein processing. Immunity. 1997;6:691–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

