Intrinsic disorder and oligomerization of the hepatitis delta virus antigen
- PMID: 20855099
- PMCID: PMC2952689
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.08.019
Intrinsic disorder and oligomerization of the hepatitis delta virus antigen
Abstract
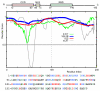
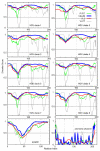
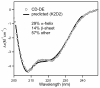
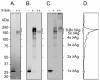
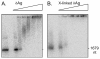
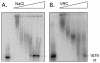
The 195 amino acid basic protein (δAg) of hepatitis delta virus (HDV) is essential for replication of the HDV RNA genome. Numerous properties have been mapped to full-length δAg and attempts made to link these to secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures. Here, for the full-size δAg, extensive intrinsic disorder was predicted using PONDR-FIT, a meta-predictor of intrinsic disorder, and evidenced by circular dichroism measurements. Most δAg amino acids are in disordered configurations with no more than 30% adopting an α-helical structure. In addition, dynamic light scattering studies indicated that purified δAg assembled into structures of as large as dodecamers. Cross-linking followed by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed hexamers to octamers for this purified δAg and at least this size for δAg found in virus-like particles. Oligomers of purified δAg were resistant to elevated NaCl and urea concentrations, and bound without specificity to RNA and single- and double-stranded DNAs.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bergmann KF, Pohl C, Gerin JL. Characterization of proteins of hepatitis delta virus. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1987;234:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Casey JL. Hepatitis delta virus. In: Compans RM, Cooper MD, Honjo T, Koprowski H, Melchers F, Oldstone MBA, Olsnes S, Potter M, Vogt PK, Wagner H, editors. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. Springer; Berlin: 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

