α-Synuclein impairs macroautophagy: implications for Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 20855506
- PMCID: PMC3101586
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201003122
α-Synuclein impairs macroautophagy: implications for Parkinson's disease
Abstract
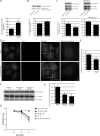
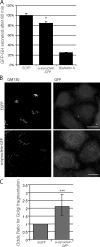
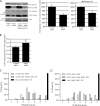
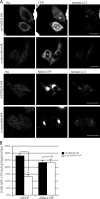
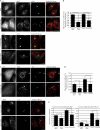
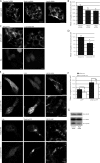
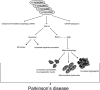
Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized pathologically by intraneuronal inclusions called Lewy bodies, largely comprised of α-synuclein. Multiplication of the α-synuclein gene locus increases α-synuclein expression and causes PD. Thus, overexpression of wild-type α-synuclein is toxic. In this study, we demonstrate that α-synuclein overexpression impairs macroautophagy in mammalian cells and in transgenic mice. Our data show that α-synuclein compromises autophagy via Rab1a inhibition and Rab1a overexpression rescues the autophagy defect caused by α-synuclein. Inhibition of autophagy by α-synuclein overexpression or Rab1a knockdown causes mislocalization of the autophagy protein, Atg9, and decreases omegasome formation. Rab1a, α-synuclein, and Atg9 all regulate formation of the omegasome, which marks autophagosome precursors.
Figures

References
-
- Axe E.L., Walker S.A., Manifava M., Chandra P., Roderick H.L., Habermann A., Griffiths G., Ktistakis N.T. 2008. Autophagosome formation from membrane compartments enriched in phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and dynamically connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 182:685–701 10.1083/jcb.200803137 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

