Hemodynamic correlates of blood pressure across the adult age spectrum: noninvasive evaluation in the Framingham Heart Study
- PMID: 20855656
- PMCID: PMC2981604
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.914507
Hemodynamic correlates of blood pressure across the adult age spectrum: noninvasive evaluation in the Framingham Heart Study
Abstract
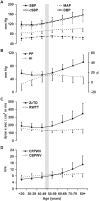
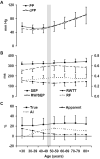
Background: Systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure are substantially higher in older adults. The relative contributions of increased forward versus reflected pressure wave amplitude or earlier arrival of the reflected wave to elevated pulse pressure remain controversial.
Methods and results: We measured proximal aortic pressure and flow, forward pressure wave amplitude, global wave reflection, reflected wave timing, and pulse wave velocity noninvasively in 6417 (age range, 19 to 90 years; 53 women) Framingham Heart Study Third Generation and Offspring participants. Variation in forward wave amplitude paralleled pulse pressure throughout adulthood. In contrast, wave reflection and pulse pressure were divergent across adulthood: In younger participants, pulse pressure was lower and wave reflection was higher with advancing age, whereas in older participants, pulse pressure was higher and wave reflection was lower with age. Reflected wave timing differed modestly across age groups despite considerable differences in pulse wave velocity. Forward wave amplitude explained 80 (central) and 66 (peripheral) of the variance in pulse pressure in younger participants (<50 years) and 90 and 84 in the older participants (≥ 50 years; all P<0.0001). In a stepwise model that evaluated age-pulse pressure relations in the full sample, the late accelerated increases in central and peripheral pulse pressure were markedly attenuated when variation in forward wave amplitude was considered.
Conclusions: Higher pulse pressure at any age and higher pulse pressure with advancing age is associated predominantly with a larger forward pressure wave. The influence of wave reflection on age-related differences in pulse pressure was minor.
Figures
References
-
- Burt VL, Whelton P, Roccella EJ, Brown C, Cutler JA, Higgins M, Horan MJ, Labarthe D. Prevalence of hypertension in the US adult population. Results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1991. Hypertension. 1995;25:305–313. - PubMed
-
- Franklin SS, Gustin W, Wong ND, Larson MG, Weber MA, Kannel WB, Levy D. Hemodynamic patterns of age-related changes in blood pressure. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1997;96:308–315. - PubMed
-
- Folkow B. Physiological aspects of primary hypertension. Physiol Rev. 1982;62:347–504. - PubMed
-
- O’Rourke MF, Nichols WW. Aortic diameter, aortic stiffness, and wave reflection increase with age and isolated systolic hypertension. Hypertension. 2005;45:652–658. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell GF, Parise H, Benjamin EJ, Larson MG, Keyes MJ, Vita JA, Vasan RS, Levy D. Changes in arterial stiffness and wave reflection with advancing age in healthy men and women: the Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension. 2004;43:1239–1245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL071039/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2-K24-HL04334/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076784/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060040/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080124/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL076784/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080124/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028321/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070100/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL071039/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL070100/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG028321/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL077447/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL004334/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077447/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

