TRIF mediates Toll-like receptor 5-induced signaling in intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 20855887
- PMCID: PMC2988362
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.158394
TRIF mediates Toll-like receptor 5-induced signaling in intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
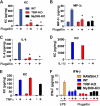
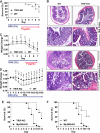
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) associate with adaptor molecules (MyD88, Mal/TIRAP, TRAM, and TRIF) to mediate signaling of host-microbial interaction. For instance, TLR4 utilizes the combination of both Mal/TIRAP-MyD88 (MyD88-dependent pathway) and TRAM-TRIF (MyD88-independent pathway). However, TLR5, the specific receptor for flagellin, is known to utilize only MyD88 to elicit inflammatory responses, and an involvement of other adaptor molecules has not been suggested in TLR5-dependent signaling. Here, we found that TRIF is involved in mediating TLR5-induced nuclear factor κB (NFκB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), specifically JNK1/2 and ERK1/2, activation in intestinal epithelial cells. TLR5 activation by flagellin permits the physical interaction between TLR5 and TRIF in human colonic epithelial cells (NCM460), whereas TLR5 does not interact with TRAM upon flagellin stimulation. Both primary intestinal epithelial cells from TRIF-KO mice and TRIF-silenced NCM460 cells significantly reduced flagellin-induced NFκB (p105 and p65), JNK1/2, and ERK1/2 activation compared with control cells. However, p38 activation by flagellin was preserved in these TRIF-deficient cells. TRIF-KO intestinal epithelial cells exhibited substantially reduced inflammatory cytokine (keratinocyte-derived cytokine, macrophage inflammatory protein 3α, and IL-6) expression upon flagellin, whereas control cells from TRIF-WT mice showed robust cytokine expression by flagellin. Compare with TRIF-WT mice, TRIF-KO mice were resistant to in vivo intestinal inflammatory responses: flagellin-mediated exacerbation of colonic inflammation and dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis. We conclude that in addition to MyD88, TRIF mediates TLR5-dependent responses and, thereby regulates inflammatory responses elicited by flagellin/TLR5 engagement. Our findings suggest an important role of TRIF in regulating host-microbial communication via TLR5 in the gut epithelium.
Figures

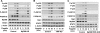


Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor 5 engagement induces interleukin-17C expression in intestinal epithelial cells.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012 Dec;32(12):583-91. doi: 10.1089/jir.2012.0053. Epub 2012 Sep 20. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012. PMID: 22994872 Free PMC article.
-
The role of TRIF protein in regulating the proliferation and antigen presentation ability of myeloid dendritic cells through the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in chronic low-grade inflammation of intestinal mucosa mediated by flagellin-TLR5 complex signal.PeerJ. 2024 Jan 2;12:e16716. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16716. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38188180 Free PMC article.
-
TRIF modulates TLR5-dependent responses by inducing proteolytic degradation of TLR5.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 9;285(28):21382-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115022. Epub 2010 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20452988 Free PMC article.
-
AsialoGM1 and TLR5 cooperate in flagellin-induced nucleotide signaling to activate Erk1/2.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006 Jun;34(6):653-60. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0441OC. Epub 2006 Jan 26. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16439799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Toll-interleukin 1 receptor mediated signaling.J Mol Med (Berl). 2005 Apr;83(4):258-66. doi: 10.1007/s00109-004-0622-4. Epub 2005 Jan 21. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15662540 Review.
Cited by
-
TLR5 expression in the small intestine depends on the adaptors MyD88 and TRIF, but is independent of the enteric microbiota.Gut Microbes. 2015;6(3):202-6. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2015.1034417. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Gut Microbes. 2015. PMID: 25923903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Provides Insights into the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Synthesis Regulation of Fat-1 Transgenic Sheep.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 7;21(3):1121. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031121. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32046209 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide: basic biochemistry, intracellular signaling, and physiological impacts in the gut.Intest Res. 2014 Apr;12(2):90-5. doi: 10.5217/ir.2014.12.2.90. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Intest Res. 2014. PMID: 25349574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling Mediated by Toll-Like Receptor 5 Sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Flagellin Influences IL-1β and IL-18 Production by Primary Fibroblasts Derived from the Human Cornea.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Apr 19;7:130. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00130. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28469996 Free PMC article.
-
The TLR4-TRIF pathway can protect against the development of experimental allergic asthma.Immunology. 2017 Sep;152(1):138-149. doi: 10.1111/imm.12755. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 28502093 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

