HNK-1 epitope-carrying tenascin-C spliced variant regulates the proliferation of mouse embryonic neural stem cells
- PMID: 20855890
- PMCID: PMC2988335
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.157081
HNK-1 epitope-carrying tenascin-C spliced variant regulates the proliferation of mouse embryonic neural stem cells
Abstract
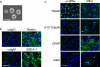
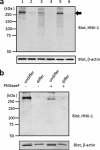
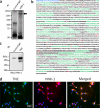
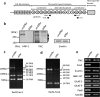
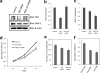
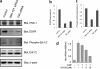
Neural stem cells (NSCs) possess high proliferative potential and the capacity for self-renewal with retention of multipotency to differentiate into neuronal and glial cells. NSCs are the source for neurogenesis during central nervous system development from fetal and adult stages. Although the human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) carbohydrate epitope is expressed predominantly in the nervous system and involved in intercellular adhesion, cell migration, and synaptic plasticity, the expression patterns and functional roles of HNK-1-containing glycoconjugates in NSCs have not been fully recognized. We found that HNK-1 was expressed in embryonic mouse NSCs and that this expression was lost during the process of differentiation. Based on proteomics analysis, it was revealed that the HNK-1 epitopes were almost exclusively displayed on an extracellular matrix protein, tenascin-C (TNC), in the mouse embryonic NSCs. Furthermore, the HNK-1 epitope was found to be present only on the largest isoform of the TNC molecules. In addition, the expression of HNK-1 was dependent on expression of the largest TNC variant but not by enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of HNK-1. By knocking down HNK-1 sulfotransferase or TNC by small interfering RNA, we further demonstrated that HNK-1 on TNC was involved in the proliferation of NSCs via modulation of the expression level of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Our finding provides insights into the function of HNK-1 carbohydrate epitopes in NSCs to maintain stemness during neural development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Site-specific HNK-1 epitope on alternatively spliced fibronectin type-III repeats in tenascin-C promotes neurite outgrowth of hippocampal neurons through contactin-1.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 10;14(1):e0210193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210193. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30629639 Free PMC article.
-
The role of human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) carbohydrate in neuronal plasticity and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Oct;1861(10):2455-2461. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.06.025. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 28709864 Review.
-
A Sulfated Glycosaminoglycan Linkage Region is a Novel Type of Human Natural Killer-1 (HNK-1) Epitope Expressed on Aggrecan in Perineuronal Nets.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 10;10(12):e0144560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144560. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26659409 Free PMC article.
-
The extracellular matrix molecule tenascin-R and its HNK-1 carbohydrate modulate perisomatic inhibition and long-term potentiation in the CA1 region of the hippocampus.Eur J Neurosci. 2000 Sep;12(9):3331-42. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00216.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10998116
-
Regulated expression and neural functions of human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) carbohydrate.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Dec;69(24):4135-47. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1036-z. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22669261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Astrocytes as a source for extracellular matrix molecules and cytokines.Front Pharmacol. 2012 Jun 26;3:120. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00120. eCollection 2012. Front Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22740833 Free PMC article.
-
Neural glycomics: the sweet side of nervous system functions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jan;78(1):93-116. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03578-9. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32613283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Extracellular Matrix Glycoprotein Tenascin C and Adult Neurogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 29;9:674199. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.674199. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33996833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matricellular protein tenascin C: Implications in glioma progression, gliomagenesis, and treatment.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 12;12:971462. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.971462. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36033448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression Patterns of Extracellular Matrix Proteins during Posterior Commissure Development.Front Neuroanat. 2016 Sep 28;10:89. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2016.00089. eCollection 2016. Front Neuroanat. 2016. PMID: 27733818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gage F. H. (2000) Science 287, 1433–1438 - PubMed
-
- McKay R. (1997) Science 276, 66–71 - PubMed
-
- Temple S., Alvarez-Buylla A. (1999) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 9, 135–141 - PubMed
-
- Campos L. S., Leone D. P., Relvas J. B., Brakebusch C., Fässler R., Suter U., ffrench-Constant C. (2004) Development 131, 3433–3444 - PubMed
-
- Learish R. D., Bruss M. D., Haak-Frendscho M. (2000) Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 122, 97–109 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

