Induction of ER stress in macrophages of tuberculosis granulomas
- PMID: 20856677
- PMCID: PMC2939897
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012772
Induction of ER stress in macrophages of tuberculosis granulomas
Abstract
Background: The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress pathway known as the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) is an adaptive survival pathway that protects cells from the buildup of misfolded proteins, but under certain circumstances it can lead to apoptosis. ER stress has been causally associated with macrophage apoptosis in advanced atherosclerosis of mice and humans. Because atherosclerosis shares certain features with tuberculosis (TB) with regard to lesional macrophage accumulation, foam cell formation, and apoptosis, we investigated if the ER stress pathway is activated during TB infection.
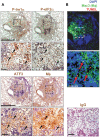
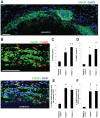
Principal findings: Here we show that ER stress markers such as C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP; also known as GADD153), phosphorylated inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha (Ire1α) and eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2α), and activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) are expressed in macrophage-rich areas of granulomas in lungs of mice infected with virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). These areas were also positive for numerous apoptotic cells as assayed by TUNEL. Microarray analysis of human caseous TB granulomas isolated by laser capture microdissection reveal that 73% of genes involved in the UPR are upregulated at the mRNA transcript level. The expression of two ER stress markers, ATF3 and CHOP, were also increased in macrophages of human TB granulomas when assayed by immunohistochemistry. CHOP has been causally associated with ER stress-induced macrophage apoptosis. We found that apoptosis was more abundant in granulomas as compared to non-granulomatous tissue isolated from patients with pulmonary TB, and apoptosis correlated with CHOP expression in areas surrounding the centralized areas of caseation.
Conclusions: In summary, ER stress is induced in macrophages of TB granulomas in areas where apoptotic cells accumulate in mice and humans. Although macrophage apoptosis is generally thought to be beneficial in initially protecting the host from Mtb infection, death of infected macrophages in advanced granulomas might favor dissemination of the bacteria. Therefore future work is needed to determine if ER-stress is causative for apoptosis and plays a role in the host response to infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC. Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:1013–1030. - PubMed
-
- Malhotra J, Kaufman R. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress: A vicious cycle or double edged sword. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling. 2007;9:2277–2294. - PubMed
-
- Tamaki N, Hatano E, Taura K, Tada M, Kodama Y, et al. CHOP deficiency attenuates cholestasis-induced liver fibrosis by reduction of hepatocyte injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;294:G498–G505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

