Epigenetic mechanisms regulate stem cell expressed genes Pou5f1 and Gfra1 in a male germ cell line
- PMID: 20856864
- PMCID: PMC2939054
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012727
Epigenetic mechanisms regulate stem cell expressed genes Pou5f1 and Gfra1 in a male germ cell line
Abstract
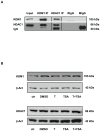
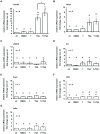
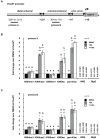
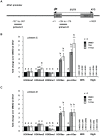
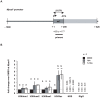
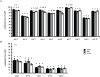
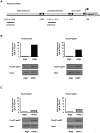
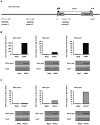
Male fertility is declining and an underlying cause may be due to environment-epigenetic interactions in developing sperm, yet nothing is known of how the epigenome controls gene expression in sperm development. Histone methylation and acetylation are dynamically regulated in spermatogenesis and are sensitive to the environment. Our objectives were to determine how histone H3 methylation and acetylation contribute to the regulation of key genes in spermatogenesis. A germ cell line, GC-1, was exposed to either the control, or the chromatin modifying drugs tranylcypromine (T), an inhibitor of the histone H3 demethylase KDM1 (lysine specific demethylase 1), or trichostatin (TSA), an inhibitor of histone deacetylases, (HDAC). Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was used to identify genes that were sensitive to treatment. As a control for specificity the Myod1 (myogenic differentiation 1) gene was analyzed. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) followed by qPCR was used to measure histone H3 methylation and acetylation at the promoters of target genes and the control, Myod1. Remarkably, the chromatin modifying treatment specifically induced the expression of spermatogonia expressed genes Pou5f1 and Gfra1. ChIP-qPCR revealed that induction of gene expression was associated with a gain in gene activating histone H3 methylation and acetylation in Pou5f1 and Gfra1 promoters, whereas CpG DNA methylation was not affected. Our data implicate a critical role for histone H3 methylation and acetylation in the regulation of genes expressed by spermatogonia--here, predominantly mediated by HDAC-containing protein complexes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of dynamic DNA methylation and histone acetylation on cPouV expression in differentiation of chick embryonic germ cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Oct 15;22(20):2725-35. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0046. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23750509 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents.Epigenetics. 2015;10(7):574-80. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1055441. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26023847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modification of Tet1 and histone methylation dynamics in dairy goat male germline stem cells.Cell Prolif. 2016 Apr;49(2):163-72. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12245. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Cell Prolif. 2016. PMID: 26988797 Free PMC article.
-
Gfra1 silencing in mouse spermatogonial stem cells results in their differentiation via the inactivation of RET tyrosine kinase.Biol Reprod. 2007 Oct;77(4):723-33. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.062513. Epub 2007 Jul 11. Biol Reprod. 2007. PMID: 17625109 Free PMC article.
-
[Epigenetic mechanisms and alcohol use disorders: a potential therapeutic target].Biol Aujourdhui. 2017;211(1):83-91. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2017014. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Biol Aujourdhui. 2017. PMID: 28682229 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Evaluation of Human Spermatogonial Stem Cells Isolated by MACS in Different Two and Three-Dimensional Culture Systems.Cell J. 2022 Aug 28;24(8):481-490. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.7888. Cell J. 2022. PMID: 36093808 Free PMC article.
-
KDM1A/LSD1 regulates the differentiation and maintenance of spermatogonia in mice.PLoS One. 2017 May 12;12(5):e0177473. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177473. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28498828 Free PMC article.
-
Unique metabolic phenotype and its transition during maturation of juvenile male germ cells.FASEB J. 2021 May;35(5):e21513. doi: 10.1096/fj.202002799R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33811704 Free PMC article.
-
Histone acetylation of the htr3a gene in the prefrontal cortex of Wistar rats regulates ethanol-seeking behavior.Neural Regen Res. 2012 May 5;7(13):1021-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.13.009. Neural Regen Res. 2012. PMID: 25722691 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin inhibits acrolein-induced apoptosis by alleviating ROS-driven mitochondrial dysfunction in male germ cells.Cell Prolif. 2014 Apr;47(2):161-71. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12091. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Cell Prolif. 2014. PMID: 24483236 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

