MPF governs the assembly and contraction of actomyosin rings by activating RhoA and MAPK during chemical-induced cytokinesis of goat oocytes
- PMID: 20856880
- PMCID: PMC2938347
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012706
MPF governs the assembly and contraction of actomyosin rings by activating RhoA and MAPK during chemical-induced cytokinesis of goat oocytes
Abstract
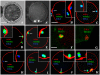
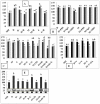
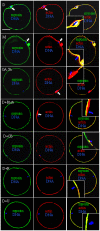
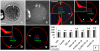
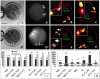
The interplay between maturation-promoting factor (MPF), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Rho GTPase during actin-myosin interactions has yet to be determined. The mechanism by which microtubule disrupters induce the formation of ooplasmic protrusion during chemical-assisted enucleation of mammalian oocytes is unknown. Moreover, a suitable model is urgently needed for the study of cytokinesis. We have established a model of chemical-induced cytokinesis and have studied the signaling events leading to cytokinesis using this model. The results suggested that microtubule inhibitors activated MPF, which induced actomyosin assembly (formation of ooplasmic protrusion) by activating RhoA and thus MAPK. While MAPK controlled actin recruitment on its own, MPF promoted myosin enrichment by activating RhoA and MAPK. A further chemical treatment of oocytes with protrusions induced constriction of the actomyosin ring by inactivating MPF while activating RhoA. In conclusion, the present data suggested that the assembly and contraction of the actomyosin ring were two separable steps: while an increase in MPF activity promoted the assembly through RhoA-mediated activation of MAPK, a decrease in MPF activity triggered contraction of the ring by activating RhoA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Barr FA, Gruneberg U. Cytokinesis: placing and making the final cut. Cell. 2007;131:847–860. - PubMed
-
- Krendel M, Zenke FT, Bokoch GM. Nucleotide exchange factor GEF-H1 mediates cross-talk between microtubules and the actin cytoskeleton. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:294–301. - PubMed
-
- Mishima M, Glotzer M. Cytokinesis. In: Lennarz WJ and Lane MD (eds) “Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry”, Elsevier Inc. Volume. 2004;1:556–561.
-
- Yamashiro S, Yamakita Y, Hosoya H, Matsumura F. Phosphorylation of non-muscle caldesmon by p34cdc2 kinase during mitosis. Nature. 1991;349:169–172. - PubMed
-
- Samaj J, Baluska F, Hirt H. From signal to cell polarity: mitogen-activated protein kinases as sensors and effectors of cytoskeleton dynamicity. J Exp Bot. 2004;55:189–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

