Regulation of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor by miR-212 and acquired cetuximab-resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 20856931
- PMCID: PMC2938338
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012702
Regulation of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor by miR-212 and acquired cetuximab-resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: We hypothesized that chronic inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) by cetuximab, a monoclonal anti-EGFR antibody, induces up-regulation of its ligands resulting in resistance and that microRNAs (miRs) play an important role in the ligand regulation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).
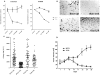
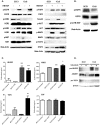
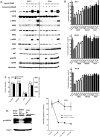
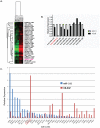
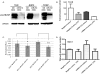
Methodology/principal findings: Genome-wide changes in gene and miR expression were determined in cetuximab-sensitive cell line, SCC1, and its resistant derivative 1Cc8 using DNA microarrays and RT-PCR. The effects of differentially expressed EGFR ligands and miRs were examined by MTS, colony formation, ELISA, and western blot assays. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and its regulator, miR-212, were differentially expressed with statistical significance when SCC1 and 1Cc8 were compared for gene and miR expression. Stimulation with HB-EGF induced cetuximab resistance in sensitive cell lines. Inhibition of HB-EGF and the addition of miR-212 mimic induced cetuximab sensitivity in resistant cell lines. MicroRNA-212 and HB-EGF expression were inversely correlated in an additional 33 HNSCC and keratinocyte cell lines. Six tumors and 46 plasma samples from HNSCC patients were examined for HB-EGF levels. HB-EGF plasma levels were lower in newly diagnosed HNSCC patients when compared to patients with recurrent disease.
Conclusions/significance: Increased expression of HB-EGF due to down-regulation of miR-212 is a possible mechanism of cetuximab resistance. The combination of EGFR ligand inhibitors or miR modulators with cetuximab may improve the clinical outcome of cetuximab therapy in HNSCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
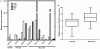
Similar articles
-
Autocrine epidermal growth factor receptor ligand production and cetuximab response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012 Mar;138(3):491-9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-011-1127-5. Epub 2011 Dec 23. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22193422 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased SMAD4 expression is associated with induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cetuximab resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(8):1252-8. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1056418. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26046389 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog signaling alters reliance on EGF receptor signaling and mediates anti-EGFR therapeutic resistance in head and neck cancer.Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 1;73(11):3381-92. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4047. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23576557 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular targeted therapies in the management of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: recent developments and perspectives.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Mar;13(3):389-402. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23092267 Review.
-
The role of cetuximab in the treatment of squamous cell cancer of the head and neck.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005 Aug;5(8):1085-93. doi: 10.1517/14712598.5.8.1085. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16050785 Review.
Cited by
-
CoGAPS matrix factorization algorithm identifies transcriptional changes in AP-2alpha target genes in feedback from therapeutic inhibition of the EGFR network.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):73845-73864. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12075. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27650546 Free PMC article.
-
Sym004, a novel EGFR antibody mixture, can overcome acquired resistance to cetuximab.Neoplasia. 2013 Oct;15(10):1196-206. doi: 10.1593/neo.131584. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 24204198 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB and stat3 transcription factor signatures differentiate HPV-positive and HPV-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2015 Oct 15;137(8):1879-89. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29558. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25857630 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional changes associated with resistance to inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor revealed using metaanalysis.BMC Cancer. 2015 May 7;15:369. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1337-3. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25948104 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression signatures modulated by epidermal growth factor receptor activation and their relationship to cetuximab resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Genomics. 2012 May 1;13:160. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-160. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22549044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arteaga C. Targeting HER1/EGFR: a molecular approach to cancer therapy. Semin Oncol. 2003;30:3–14. - PubMed
-
- Harris R, Chung E, Coffey R. EGF receptor ligands. Experimental Cell Research 2003. 2003. pp. 2–13. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Cullen BR. Transcription and processing of human microRNA precursors. Mol Cell. 2004;16:861–865. - PubMed
-
- Lund E, Guttinger S, Calado A, Dahlberg JE, Kutay U. Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science. 2004;303:95–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

