Lowered HGK expression inhibits cell invasion and adhesion in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2
- PMID: 20857524
- PMCID: PMC2945485
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4541
Lowered HGK expression inhibits cell invasion and adhesion in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of RNA interference targeting hepatocyte progenitor kinase-like kinase (HGK) in the invasion and adhesion of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line HepG2.
Methods: Three paired insert DNA fragments specific to HGK gene and one negative control DNA fragment were synthesized and inserted into RNAi-Ready pSIREN-RetroQ-ZsGreen vector. Western blotting assay and real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) were used to screen the vector with a highest inhibitory rate. The vector was used to generate recombinant retrovirus specific to HGK. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2h-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was used to examine cell growth; wound closure assay and cell adhesion assay were employed to investigate cell migration and adhesion respectively; and transwell assay and three-dimensional culture invasion assay were used to detect cell invasion. The expressions of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9 and nuclear factor (NF)-κB were detected by Western blotting assay.
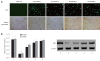
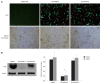
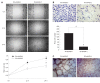
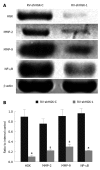
Results: The real time RT-PCR and Western blotting assay showed that cells transfected with retrovirus mediating RNAi targeting of HGK (RV-shHGK)-1 vector had the strongest inhibition of HGK protein, with an inhibition rate of 76%, and this vector was used to generate recombinant retrovirus RV-shHGK-1. Cell adhesion assay and MTT assay found that cell adhesion and growth of the cells infected with RV-shHGK-1 were significantly lower than those of the control cells (P < 0.05). Wound closure assay, transwell assay and three-dimensional culture invasion assay showed that the cell invasiveness was significantly less in HGK knockdown cells than in the control cells (P < 0.05). The expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9 and NF-κB were inhibited in HepG2 cells infected with RV-shHGK-1.
Conclusion: Down-regulation of HGK can obviously inhibit the migration and invasion of HepG2 cells in vitro. HGK may be a new therapeutic target for treatment of HCC.
Figures
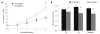
Similar articles
-
[miR-143 inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via down-regulation of TLR2 expression].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Oct;30(10):1076-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25270212 Chinese.
-
Suppressive effects of microRNA-16 on the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Dec;36(6):1713-9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2379. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26499886
-
S100A4 regulates migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells via NF-κB-dependent MMP-9 signal.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Sep;17(17):2372-82. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24065232 Clinical Trial.
-
Fibulin-5 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by down-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression.BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 12;14:938. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-938. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25494879 Free PMC article.
-
Solamargine inhibits migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 expression and activity.Toxicol In Vitro. 2015 Aug;29(5):893-900. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2015.03.012. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Toxicol In Vitro. 2015. PMID: 25819016
Cited by
-
Map4k4 Signaling Nodes in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jul;27(7):484-492. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 May 6. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27160798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of MAP4 Kinase Inhibitors as Motor Neuron-Protecting Agents.Cell Chem Biol. 2019 Dec 19;26(12):1703-1715.e37. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.10.005. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Cell Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31676236 Free PMC article.
-
The inflammatory kinase MAP4K4 promotes reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus and enhances the invasiveness of infected endothelial cells.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(11):e1003737. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003737. Epub 2013 Nov 7. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24244164 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
MAP4K4: an emerging therapeutic target in cancer.Cell Biosci. 2016 Oct 28;6:56. doi: 10.1186/s13578-016-0121-7. eCollection 2016. Cell Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27800153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Value of mRNA Expression of MAP4K Family in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan 1;18:1533033819873927. doi: 10.1177/1533033819873927. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 31522654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Urzúa U, Roby KF, Gangi LM, Cherry JM, Powell JI, Munroe DJ. Transcriptomic analysis of an in vitro murine model of ovarian carcinoma: functional similarity to the human disease and identification of prospective tumoral markers and targets. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206:594–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

