Endoscopic removal of gastric ectopic pancreas: an initial experience with endoscopic submucosal dissection
- PMID: 20857531
- PMCID: PMC2945492
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4589
Endoscopic removal of gastric ectopic pancreas: an initial experience with endoscopic submucosal dissection
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the therapeutic usefulness and safety of endoscopic resection in patients with gastric ectopic pancreas.
Methods: A total of eight patients with ectopic pancreas were included. All of them underwent endoscopic ultrasonography before endoscopic resection. Endoscopic resection was performed by two methods: endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) by the injection-and-cut technique or endoscopic mucosal dissection (ESD).
Results: We planned to perform EMR in all eight cases but EMR was successful in only four cases. In the other four cases, saline spread into surrounding normal tissues and the lesions became flattened, which made it impossible to remove them by EMR. In those four cases, we performed ESD and removed the lesions without any complications.
Conclusion: If conventional EMR is difficult to remove gastric ectopic pancreas, ESD is a feasible alternative method for successful removal.
Figures
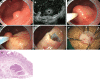
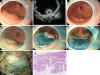
Similar articles
-
Gastric mucosal cancer smaller than 7mm can be treated with conventional endoscopic mucosal resection as effectively as with endoscopic submucosal dissection.Hepatogastroenterology. 2010 May-Jun;57(99-100):668-73. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20698247
-
Indications for the use of endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer in Japan: a comparative study with endoscopic submucosal dissection.Endoscopy. 2009 Sep;41(9):746-50. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1215010. Epub 2009 Aug 13. Endoscopy. 2009. PMID: 19681023
-
Outcome after endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in Korea.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Aug 21;17(31):3591-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i31.3591. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21987605 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer.Digestion. 2008;77 Suppl 1:23-8. doi: 10.1159/000111484. Epub 2008 Jan 18. Digestion. 2008. PMID: 18204258 Review.
-
Management of the complications of endoscopic submucosal dissection.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Aug 21;17(31):3575-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i31.3575. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21987602 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced CT and CT virtual endoscopy in diagnosis of heterotopic pancreas.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep 7;17(33):3850-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3850. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21987629 Free PMC article.
-
Magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging for gastric heterotopic pancreas.Endosc Int Open. 2018 Mar;6(3):E369-E375. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-101350. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Endosc Int Open. 2018. PMID: 29527560 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic pancreas in the stomach successfully resected by endoscopic submucosal dissection.Case Rep Med. 2015;2015:147927. doi: 10.1155/2015/147927. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Case Rep Med. 2015. PMID: 25878668 Free PMC article.
-
Endosonographic features of histologically proven gastric ectopic pancreas.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014;2014:160601. doi: 10.1155/2014/160601. Epub 2014 Oct 12. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014. PMID: 25371670 Free PMC article.
-
Interventional endoscopic ultrasound for a symptomatic pseudocyst secondary to gastric heterotopic pancreas.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Sep 14;23(34):6365-6370. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6365. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28974904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeBord JR, Majarakis JD, Nyhus LM. An unusual case of heterotopic pancreas of the stomach. Am J Surg. 1981;141:269–273. - PubMed
-
- Burke GW, Binder SC, Barron AM, Dratch PL, Umlas J. Heterotopic pancreas: gastric outlet obstruction secondary to pancreatitis and pancreatic pseudocyst. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989;84:52–55. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida T, Sakamoto A, Kuroki K, Kojo A, Watanabe H. Electrocoagulation biopsy of aberrant pancreas of the stomach. A case of aberrant gastric pancreas. Am J Gastroenterol. 1976;66:554–558. - PubMed
-
- Matsushita M, Hajiro K, Okazaki K, Takakuwa H. Gastric aberrant pancreas: EUS analysis in comparison with the histology. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;49:493–497. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Lim JS, Lee YC, Hyung WJ, Lee JH, Kim MJ, Chung JB. Endosonographic features of gastric ectopic pancreases distinguishable from mesenchymal tumors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:e301–e307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

