Roles of Sema4D and Plexin-B1 in tumor progression
- PMID: 20858260
- PMCID: PMC2955613
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-251
Roles of Sema4D and Plexin-B1 in tumor progression
Abstract
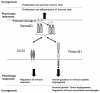
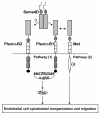
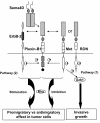
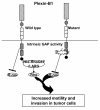
Sema4D, also known as CD100, is a protein belonging to class IV semaphorin. Its physiologic roles in the immune and nervous systems have been extensively explored. However, the roles of Sema4D have extended beyond these traditionally studied territories. Via interaction with its high affinity receptor Plexin-B1, Sema4D-Plexin-B1 involvement in tumor progression is strongly implied. Here, we critically review and delineate the Sema4D-Plexin-B1 interaction in many facets of tumor progression: tumor angiogenesis, regulation of tumor-associated macrophages and control of invasive growth. We correlate the in vitro and in vivo experimental data with the clinical study outcomes, and present a molecular mechanistic basis accounting for the intriguingly contradicting results from these recent studies.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

