Hyperpolarized 13C spectroscopic imaging informs on hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and myc activity downstream of platelet-derived growth factor receptor
- PMID: 20858719
- PMCID: PMC2948586
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0883
Hyperpolarized 13C spectroscopic imaging informs on hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and myc activity downstream of platelet-derived growth factor receptor
Abstract
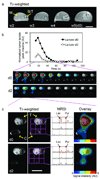
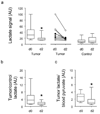
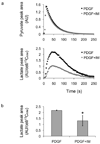
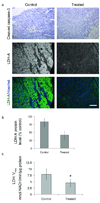
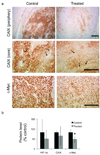
The recent development of hyperpolarized (13)C magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging provides a novel method for in vivo metabolic imaging with potential applications for detection of cancer and response to treatment. Chemotherapy-induced apoptosis was shown to decrease the flux of hyperpolarized (13)C label from pyruvate to lactate due to depletion of NADH, the coenzyme of lactate dehydrogenase. In contrast, we show here that in PC-3MM2 tumors, inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor receptor with imatinib reduces the conversion of hyperpolarized pyruvate to lactate by lowering the expression of lactate dehydrogenase itself. This was accompanied by reduced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and glutaminase, and is likely mediated by reduced expression of their transcriptional factors hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and c-Myc. Our results indicate that hyperpolarized (13)C MRSI could potentially detect the molecular effect of various cell signaling inhibitors, thus providing a radiation-free method to predict tumor response.
© 2010 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123:309–314. - PubMed
-
- DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB. The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab. 2008;7:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Boss DS, Olmos RV, Sinaasappel M, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH. Application of PET/CT in the development of novel anticancer drugs. Oncologist. 2008;13:25–38. - PubMed
-
- Gillies RJ, Robey I, Gatenby RA. Causes and consequences of increased glucose metabolism of cancers. J Nucl Med. 2008;49 Suppl 2 24S–42S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

