Electrochemical and homogeneous electron transfers to the Alzheimer amyloid-beta copper complex follow a preorganization mechanism
- PMID: 20858730
- PMCID: PMC2951405
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1011315107
Electrochemical and homogeneous electron transfers to the Alzheimer amyloid-beta copper complex follow a preorganization mechanism
Abstract
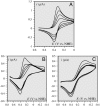
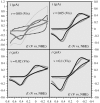
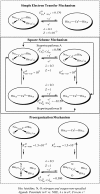
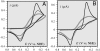
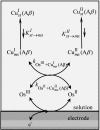
Deciphering the electron transfer reactivity characteristics of amyloid β-peptide copper complexes is an important task in connection with the role they are assumed to play in Alzheimer's disease. A systematic analysis of this question with the example of the amyloid β-peptide copper complex by means of its electrochemical current-potential responses and of its homogenous reactions with electrogenerated fast electron exchanging osmium complexes revealed a quite peculiar mechanism: The reaction proceeds through a small fraction of the complex molecules in which the peptide complex is "preorganized" so as the distances and angles in the coordination sphere to vary minimally upon electron transfer, thus involving a remarkably small reorganization energy (0.3 eV). This preorganization mechanism and its consequences on the reactivity should be taken into account for reactions involving dioxygen and hydrogen peroxide that are considered to be important in Alzheimer's disease through the production of harmful reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gaggelli E, Kozlowski H, Valensin D, Valensin G. Copper homeostasis and neurodegenerative disorders (Alzheimer’s, Prion, and Parkinson’s diseases and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) Chem Rev. 2006;106:1995–2044. - PubMed
-
- Barnham KJ, Bush AI. Metals in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2008;12:222–228. - PubMed
-
- Smith DG, Cappai R, Barnham KJ. The redox chemistry of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid b peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2007;1768:1976–1990. - PubMed
-
- Hureau C, Faller P. Aβ-mediated ROS production by the Cu ions: Structural insights, mechanisms and relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Biochimie. 2009;91:1212–1217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

