Decidual PTEN expression is required for trophoblast invasion in the mouse
- PMID: 20858757
- PMCID: PMC3006249
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00255.2010
Decidual PTEN expression is required for trophoblast invasion in the mouse
Abstract
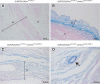
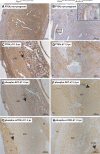
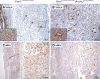
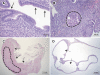
Trophoblast invasion likely depends on complex cross talk between the fetal and maternal tissues and may involve the modulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT signaling activity in maternal decidual cells. In this report, we studied implantation in Pten(tm1Hwu/tm1Hwu);Amhr2(tm3(cre)Bhr/+) mice, which lack the PI3K signaling antagonist gene Pten in myometrial and stromal/decidual cells. Primiparous Pten(tm1Hwu/tm1Hwu);Amhr2(tm3(cre)Bhr/+) mice were found to be subfertile because of increased fetal mortality at e11.5. Histopathological analyses revealed a failure of decidual regression in these mice, accompanied by reduced or absent invasion of fetal trophoblast glycogen cells and giant cells, abnormal development of the placental labyrinth, and frequent apparent intrauterine fetal growth restriction. Unexpectedly, the loss of phosphate and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) expression in Pten(tm1Hwu/tm1Hwu);Amhr2(tm3(cre)Bhr/+) decidual cells was not accompanied by a detectable increase in AKT phosphorylation or altered expression or activation of PI3K/AKT downstream effectors such as mammalian target of rapamycin or glycogen synthase kinase-3β. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated nick end labeling and bromodeoxyuridine incorporation analyses attributed to the lack of decidual regression mainly to decreased apoptosis in Pten(tm1Hwu/tm1Hwu);Amhr2(tm3(cre)Bhr/+) decidual cells, rather than to increased proliferation. Remodeling of the maternal vasculature was delayed in Pten(tm1Hwu/tm1Hwu);Amhr2(tm3(cre)Bhr/+) uteri at e11.5, as evidenced by persistence of vascular smooth muscle and decreased infiltration of uterine natural killer cells. In addition, thickening of the myometrium and disorganization of the muscle fibers were observed before and throughout gestation. Almost all Pten(tm1Hwu/tm1Hwu);Amhr2(tm3(cre)Bhr/+) mice failed to carry a second litter to term, apparently attributable to endometrial hyperplasia and uterine infections. Together, these data demonstrate novel roles of PTEN in the mammalian uterus and its requirement for proper trophoblast invasion and decidual regression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of WNT/CTNNB1 and PI3K/AKT signaling in testicular stromal cells causes granulosa cell tumor of the testis.Carcinogenesis. 2009 May;30(5):869-78. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp051. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Carcinogenesis. 2009. PMID: 19237610 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of Pten loss and WNT/CTNNB1 signaling pathway activation in ovarian granulosa cell tumor development and progression.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Nov;29(11):2062-72. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn186. Epub 2008 Aug 6. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18687666 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatase of regenerating liver 2 (PRL2) is essential for placental development by down-regulating PTEN (Phosphatase and Tensin Homologue Deleted on Chromosome 10) and activating Akt protein.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 14;287(38):32172-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.393462. Epub 2012 Jul 12. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22791713 Free PMC article.
-
The role of decidual cells in uterine hemostasis, menstruation, inflammation, adverse pregnancy outcomes and abnormal uterine bleeding.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Jun;22(4):497-515. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmw004. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 26912000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical growth factors and signalling pathways controlling human trophoblast invasion.Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(2-3):269-80. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.082769mk. Int J Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 19876833 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stromal liver kinase B1 [STK11] signaling loss induces oviductal adenomas and endometrial cancer by activating mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(8):e1002906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002906. Epub 2012 Aug 16. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22916036 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK) 3 in pregnancy and parturition: a systematic review of literature.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020 Jun;33(11):1946-1957. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2018.1531843. Epub 2019 Jan 6. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020. PMID: 30278798 Free PMC article.
-
Positive regulation of placentation by L-amino acid transporter-1 (lat1) in pregnant mice.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Sep 1;10(9):9551-9558. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966831 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Deletion of PTEN in Kisspeptin Cells Results in Brain Region- and Sex-Specific Effects on Kisspeptin Expression and Gonadotropin Release.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 19;21(6):2107. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062107. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32204355 Free PMC article.
-
STX2 Promotes Trophoblast Growth, Migration, and Invasion Through Activation of the PI3K-AKT Pathway in Preeclampsia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 6;9:615973. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.615973. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34295885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arango NA, Szotek PP, Manganaro TF, Oliva E, Donahoe PK, Teixeira J. Conditional deletion of beta-catenin in the mesenchyme of the developing mouse uterus results in a switch to adipogenesis in the myometrium. Dev Biol 288: 276–283, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bischof P, Campana A. Molecular mediators of implantation. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 14: 801–814, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Bischof P, Meisser A, Campana A. Biochemistry and molecular biology of trophoblast invasion. Ann NY Acad Sci 943: 157–162, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Leal JF, Carnero A. PTEN, more than the AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis 28: 1379–1386, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Brosens IA. The utero-placental vessels at term- the distribution and extent of the physiological changes. Trophoblast Res 3: 61–67, 1988
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

