Diet and caries-associated bacteria in severe early childhood caries
- PMID: 20858780
- PMCID: PMC2954266
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034510376543
Diet and caries-associated bacteria in severe early childhood caries
Abstract
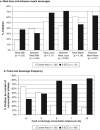
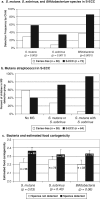
Frequent consumption of cariogenic foods and bacterial infection are risk factors for early childhood caries (ECC). This study hypothesized that a short diet survey focused on frequency of foods, categorized by putative cariogenicity, would differentiate severe ECC (S-ECC) from caries-free children. Children's diets were obtained by survey and plaque bacteria detected by PCR from 72 S-ECC and 38 caries-free children. S-ECC children had higher scores for between-meal juice (p < 0.01), solid-retentive foods (p < 0.001), eating frequency (p < 0.005), and estimated food cariogenicity (p < 0.0001) than caries-free children. S-ECC children with lesion recurrence ate fewer putative caries-protective foods than children without new lesions. Streptococcus mutans (p < 0.005), Streptococcus sobrinus (p < 0.005), and Bifidobacteria (p < 0.0001) were associated with S-ECC, and S. mutans with S. sobrinus was associated with lesion recurrence (p < 0.05). S. mutans-positive children had higher food cariogenicity scores. Food frequency, putative cariogenicity, and S. mutans were associated with S-ECC individually and in combination.
Figures
Comment in
-
Diet may be Associated with the Detection of Cariogenic Bacteria in Children with Early Childhood Caries.J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2011 Sep;11(3):153-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jebdp.2011.06.015. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2011. PMID: 21855819 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aligne CA, Moss ME, Auinger P, Weitzman M. (2003). Association of pediatric dental caries with passive smoking. JAMA 289:1258-1264 - PubMed
-
- Almeida AG, Roseman MM, Sheff M, Huntington N, Hughes CV. (2000). Future caries susceptibility in children with early childhood caries following treatment under general anesthesia. Pediatr Dent 22:302-306 - PubMed
-
- Arcella D, Ottolenghi L, Polimeni A, Leclercq C. (2002). The relationship between frequency of carbohydrates intake and dental caries: a cross-sectional study in Italian teenagers. Public Health Nutr 5:553-560 - PubMed
-
- Bankel M, Eriksson UC, Robertson A, Köhler B. (2006). Caries and associated factors in a group of Swedish children 2-3 years of age. Swed Dent J 30:137-146 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

