Synthetic lethal screen of an EGFR-centered network to improve targeted therapies
- PMID: 20858866
- PMCID: PMC2950064
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2001083
Synthetic lethal screen of an EGFR-centered network to improve targeted therapies
Abstract
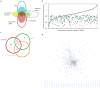
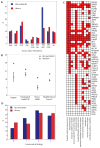
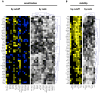
Intrinsic and acquired cellular resistance factors limit the efficacy of most targeted cancer therapeutics. Synthetic lethal screens in lower eukaryotes suggest that networks of genes closely linked to therapeutic targets would be enriched for determinants of drug resistance. We developed a protein network centered on the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which is a validated cancer therapeutic target, and used small interfering RNA screening to comparatively probe this network for proteins that regulate the effectiveness of both EGFR-targeted agents and nonspecific cytotoxic agents. We identified subnetworks of proteins influencing resistance, with putative resistance determinants enriched among proteins that interacted with proteins at the core of the network. We found that clinically relevant drugs targeting proteins connected in the EGFR network, such as protein kinase C or Aurora kinase A, or the transcriptional regulator signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), synergized with EGFR antagonists to reduce cell viability and tumor size, suggesting the potential for a direct path to clinical exploitation. Such a focused approach can potentially improve the coherent design of combination cancer therapies.
Figures
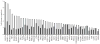



References
-
- Lievre A, Bachet JB, Le Corre D, Boige V, Landi B, Emile JF, Cote JF, Tomasic G, Penna C, Ducreux M, Rougier P, Penault-Llorca F, Laurent-Puig P. KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2006 Apr 15;66:3992. - PubMed
-
- Friedman A, Perrimon N. Genetic screening for signal transduction in the era of network biology. Cell. 2007 Jan 26;128:225. - PubMed
-
- Barabasi AL, Albert R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science. 1999 Oct 15;286:509. - PubMed
-
- Hartwell LH, Hopfield JJ, Leibler S, Murray AW. From molecular to modular cell biology. Nature. 1999 Dec 2;402:C47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

