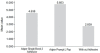Comparison of the shear bond strength of RMGIC to a resin composite using different adhesive systems: An in vitro study
- PMID: 20859480
- PMCID: PMC2936095
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-0707.66716
Comparison of the shear bond strength of RMGIC to a resin composite using different adhesive systems: An in vitro study
Abstract
Aim: This study evaluated and compared the role of newer dental adhesives to bond composite resin to the resin modified glass ionomer (RMGIC) liner.
Materials and methods: Thirty-six specimens were prepared on acrylic blocks, with wells prepared in it by drilling holes, to retain the RMGIC. The specimens were randomly divided into three groups of 12 specimens each. In group I, a thin layer of an adhesive, which was a Total-etch type (Adper Single bond-2), was applied between RMGIC and the composite resin. Ingroup II, a Self-Etch adhesive (Adper prompt-L pop) was applied, and in group III there was no application of any adhesive between RMGIC and the composite resin. After curing all the specimens, the shear bond strength was measured using an Instron universal testing machine.
Results: The results were drawn and tabulated using ANOVA-fishers and Tukey's statistical tests. The maximum shear bond strength values were recorded in group II specimens with the self-etch adhesive (Adper prompt-L pop), showing a mean value of 5.826 when compared to the group I adhesive-Total-etch type with a mean shear bond strength of 4.6380, while group III specimens, where no adhesive was used, showed a minimum mean shear bond strength of 2.8385. There was a great and significant difference between group I and group II (P value 0.003), whereas, both group I and group II showed a vast and significant difference from group III (P value 0 - 001).
Conclusion: Hence, this present study concludes that application of Self-Etch adhesive (Adper prompt-L pop) in between RMGIC and composite resin increases the shear bond strength between RMGIC and the resin composites, as compared to the Total-etch type adhesives (Adper Single Bond 2), as well as, without application of the adhesive agent.
Keywords: Sandwich technique; Self-Etch adhesive; Total-etch adhesive.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative study to evaluate shear bond strength of RMGIC to composite resin using different adhesive systems.Contemp Clin Dent. 2012 Jul;3(3):252-5. doi: 10.4103/0976-237X.103613. Contemp Clin Dent. 2012. PMID: 23293476 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Shear Bond Strength between Nanofilled Composite Bonded to Glass-ionomer Cement Using Self-etch Adhesive with Different pHs and Total-Etch Adhesive.J Dent (Shiraz). 2016 Mar;17(1):1-6. J Dent (Shiraz). 2016. PMID: 26966701 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of saliva contamination and decontamination procedures on shear bond strength of self-etch dentine bonding systems: An in vitro study.J Conserv Dent. 2010 Apr;13(2):71-5. doi: 10.4103/0972-0707.66714. J Conserv Dent. 2010. PMID: 20859478 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of total-etch and self-etch adhesives on the bond strength of composite to glass-ionomer cement/resin-modified glass-ionomer cement in the sandwich technique - A systematic review.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2021 Sep 25;18:72. doi: 10.4103/1735-3327.326645. eCollection 2021. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2021. PMID: 34760063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of bond strength of self-adhesive and self-etch or total-etch resin cement to zirconia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024 Feb;27(2):113-125. doi: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_225_23. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024. PMID: 38463466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Nanosilver Fluoride Application on the Microtensile Bond Strength of Glass Ionomer Cement and Resin-modified Glass Ionomer Cement on Primary Carious Dentin: An In Vitro Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024 May;17(5):565-569. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2863. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024. PMID: 39355194 Free PMC article.
-
Shear Bond Strength Evaluation of Resin Composite Bonded to GIC Using Different Adhesives.J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 Jan;9(1):ZC27-9. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/10224.5462. Epub 2015 Jan 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015. PMID: 25738081 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of microleakage in posterior nanocomposite restorations with adhesive liners.J Conserv Dent. 2011 Apr;14(2):178-81. doi: 10.4103/0972-0707.82631. J Conserv Dent. 2011. PMID: 21814362 Free PMC article.
-
Shear Bond Strength of Bulk-Fill Composites to Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Evaluated by Different Adhesion Protocols.Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2020 Sep 16;12:367-375. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S273842. eCollection 2020. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2020. PMID: 32982465 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Self-etching Adhesives on the Bond Strength of Glass-Ionomer Cements.J Dent (Tehran). 2014 Nov;11(6):680-6. Epub 2014 Nov 30. J Dent (Tehran). 2014. PMID: 25628698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson AD, Kent BE. The glass ionomer cement: A new transluscent dental filling material. J Appl Chem Biotechno. 1971;21:313.
-
- Hotz P, McLean JW, Sneed I, Wilson AD. The bonding of glass ionomer cements to metal and tooth substrates. Br Dent J. 1977;142:41–7. - PubMed
-
- Swartz ML, Phillips RW, Clark HE. Long term fluoride release from glass-ionomer cements. J Dent Res. 1984;63:158–60. - PubMed
-
- Wilson AD, McLean JW. Glass ionomer cements. Chicago: Quintessence Publishing Co; 1988.
-
- Craig RG. Restorative dental materials. 8th ed. vol. 53. St. Louis: CV. Mosby Co; 1989. p. 256.