Radiosynthesis and initial in vitro evaluation of [18F]F-PEG6-IPQA--a novel PET radiotracer for imaging EGFR expression-activity in lung carcinomas
- PMID: 20859697
- PMCID: PMC6130206
- DOI: 10.1007/s11307-010-0408-8
Radiosynthesis and initial in vitro evaluation of [18F]F-PEG6-IPQA--a novel PET radiotracer for imaging EGFR expression-activity in lung carcinomas
Abstract
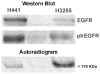
Introduction: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted therapies with antibodies and small molecular EGFR kinase inhibitors have shown poor efficacy in unselected populations of patients with advanced non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC). In contrast, patients with overexpression of EGFR and activating mutations in EGFR kinase domain demonstrated improved responses to EGFR kinase inhibitors. Therefore, we have developed a novel radiotracer, [(18)F]F-PEG(6)-IPQA for PET imaging of EGFR expression-activity in NSCLC, and have described its radiosynthesis and in vitro evaluation in two NSCLC cell lines with wild-type and L858R active mutant EGFR.
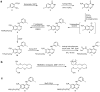
Methods: A mesylate precursor was synthesized in multiple steps and radiofluorinated using K(18)F/Kryptofix. The fluorinated intermediate compound was reduced to an amino derivative then treated with acryloyl isobutyl carbonate, followed by purification by HPLC to obtain the desired product.
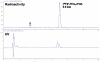
Results: Decay-corrected radiochemical yields of [(18)F]F-PEG(6)-IPQA were 3.9-17.6%, with an average of 9.0% (n = 11). Radiochemical purity was >97% with specific activity of 34 GBq/μmol (mean value, n = 10) at the end of synthesis. The accumulation of [(18)F]F-PEG(6)-IPQA in H3255 cells was ten-fold higher than in H441 cells, despite a two-fold lower level of activated phospho-EGFR expression in H3255 cells compared with H441 cells. The accumulation of [(18)F]F-PEG(6)-IPQA in both cell lines was significantly decreased in the presence of a small molecular EGFR kinase inhibitor, Iressa, at 100 μM concentration in culture medium.
Conclusion: We have synthesized [(18)F]F-PEG(6)-IPQA and demonstrated its highly selective accumulation in active mutant L858R EGFR-expressing NSCLC cells in vitro. Further in vivo studies are warranted to assess the ability of PET imaging with [(18)F]F-PEG(6)-IPQA to discriminate the active mutant L858R EGFR-expressing NSCLC that are sensitive to therapy with EGFR kinase inhibitors vs NSCLC that express wild-type EGFR.
Figures


References
-
- ACS Cancer Reference Information. 2009 http://wwwcancerorg/docroot/CRI/content/CRI_2_4_1x_What_Are_the_Key_Stat...
-
- Mishani E, Abourbeh G. Cancer molecular imaging: radio-nuclide-based biomarkers of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7:1755–1772. - PubMed
-
- Mishani E, Hagooly A. Strategies for molecular imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase in cancer. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:1199–1202. - PubMed
-
- Bonasera TA, Ortu G, Rozen Y, Krais R, Freedman NM, Chisin R, Gazit A, Levitzki A, Mishani E. Potential (18)F-labeled biomarkers for epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Nucl Med Biol. 2001;28:359–374. - PubMed
-
- Ortu G, Ben-David I, Rozen Y, Freedman NM, Chisin R, Levitzki A, Mishani E. Labeled EGFr-TK irreversible inhibitor (ML03): in vitro and in vivo properties, potential as PET biomarker for cancer and feasibility as anticancer drug. Int J Cancer. 2002;101:360–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

