Type B coxsackieviruses and their interactions with the innate and adaptive immune systems
- PMID: 20860480
- PMCID: PMC3045535
- DOI: 10.2217/fmb.10.101
Type B coxsackieviruses and their interactions with the innate and adaptive immune systems
Abstract
Coxsackieviruses are important human pathogens, and their interactions with the innate and adaptive immune systems are of particular interest. Many viruses evade some aspects of the innate response, but coxsackieviruses go a step further by actively inducing, and then exploiting, some features of the host cell response. Furthermore, while most viruses encode proteins that hinder the effector functions of adaptive immunity, coxsackieviruses and their cousins demonstrate a unique capacity to almost completely evade the attention of naive CD8(+) T cells. In this artcle, we discuss the above phenomena, describe the current status of research in the field, and present several testable hypotheses regarding possible links between virus infection, innate immune sensing and disease.
Figures
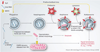
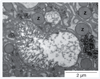
Similar articles
-
Host immune responses to coxsackievirus B3.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;323:199-221. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75546-3_9. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18357771 Review.
-
Molecular biology and pathogenesis of viral myocarditis.Annu Rev Pathol. 2008;3:127-55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.151534. Annu Rev Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18039131 Review.
-
The innate immune response: an important partner in shaping coxsackievirus-mediated autoimmunity.J Innate Immun. 2009;1(5):421-34. doi: 10.1159/000226247. Epub 2009 Jun 24. J Innate Immun. 2009. PMID: 20375600 Review.
-
Manipulating intestinal immunity and microflora: an alternative solution to viral myocarditis?Future Microbiol. 2012 Oct;7(10):1207-16. doi: 10.2217/fmb.12.96. Future Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23030425 Review.
-
Immunology in the clinic review series; focus on type 1 diabetes and viruses: role of antibodies enhancing the infection with Coxsackievirus-B in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes.Clin Exp Immunol. 2012 Apr;168(1):47-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04559.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22385236 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Essential Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Enterovirus Infection: From Basic Mechanisms to Clinical Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 12;22(6):2904. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062904. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33809362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRIM56 restricts Coxsackievirus B infection by mediating the ubiquitination of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 3D.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Sep 30;20(9):e1012594. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012594. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39348396 Free PMC article.
-
Coagulation, protease-activated receptors, and viral myocarditis.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2014 Mar;7(2):203-11. doi: 10.1007/s12265-013-9515-7. Epub 2013 Nov 8. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2014. PMID: 24203054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Type III Interferon Expression in Intestinal Epithelial Cells-A Strategy Used by Coxsackie B Virus to Evade the Host's Innate Immune Response at the Primary Site of Infection?Microorganisms. 2021 Jan 5;9(1):105. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010105. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33466313 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoglycin-induced VEGF Inhibition Enhances T Lymphocytes Infiltrating in Colorectal Cancer.EBioMedicine. 2018 Aug;34:35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.021. Epub 2018 Jul 21. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 30037719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Modlin JF, Rotbart HA. Group B coxsackie disease in children. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1997;223:53–80. - PubMed
-
- Whitton JL. Immunopathology during coxsackievirus infection. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 2002;24:201–213. - PubMed
-
- Romero JR. Pediatric group B coxsackievirus infections. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008;323:223–239. - PubMed
-
- Sole MJ, Liu P. Viral myocarditis: a paradigm for understanding the pathogenesis and treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1993;22:A99–A105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
