The glucose triad and its role in comprehensive glycaemic control: current status, future management
- PMID: 20860758
- PMCID: PMC3036818
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2010.02517.x
The glucose triad and its role in comprehensive glycaemic control: current status, future management
Abstract
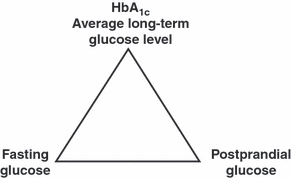
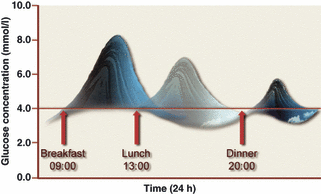
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes across the world has been described as a global pandemic. Despite significant efforts to limit both the increase in the number of cases and the long-term impact on morbidity and mortality, the total number of people with diabetes is projected to continue to rise and most patients still fail to achieve adequate glycaemic control. Optimal management of type 2 diabetes requires an understanding of the relationships between glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA(1c)), fasting plasma glucose and postprandial glucose (the glucose triad), and how these change during development and progression of the disease. Early and sustained control of glycaemia remains important in the management of type 2 diabetes. The contribution of postprandial glucose levels to overall glycaemic control and the role of postprandial glucose targets in disease management are currently debated. However, many patients do not reach HbA(1C) targets set according to published guidelines. As recent data suggest, if driving HbA(1C) down to lower target levels is not the answer, what other factors involved in glucose homeostasis can or should be targeted? Has the time come to change the treatment paradigm to include awareness of the components of the glucose triad, the existence of glucose variability and their potential influence on the choice of pharmacological treatment? It is becomingly increasingly clear that physicians are likely to have to consider plasma glucose levels both after the overnight fast and after meals as well as the variability of glucose levels, in order to achieve optimal glycaemic control for each patient. When antidiabetic therapy is initiated, physicians may need to consider selection of agents that target both fasting and postprandial hyperglycaemia.
© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 1998;352:837–53. - PubMed
-
- Laakso M, Kuusisto J. Epidemiological evidence for the association of hyperglycaemia and atherosclerotic vascular disease in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Ann Med. 1996;28:415–8. - PubMed
-
- Selvin E, Marinopoulos S, Berkenblit G, et al. Meta-analysis: glycosylated hemoglobin and cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 2004;141:421–31. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Standards of medical care in diabetes – 2008. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(Suppl. 1):S12–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

