Electrocardiographic changes with the onset of diabetes and the impact of aerobic exercise training in the Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) rat
- PMID: 20860788
- PMCID: PMC2954909
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-9-56
Electrocardiographic changes with the onset of diabetes and the impact of aerobic exercise training in the Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) rat
Abstract
Background: Early markers of diabetic autonomic neuropathy (DAN) in an electrocardiogram (ECG) include elevated R wave amplitudes, widening of QTc intervals and decreased heart rate variability (HRV). The severity of DAN has a direct relationship with mortality risk. Aerobic exercise training is a common recommendation for the delay and possible reversal of cardiac dysfunction. Limited research exists on ECG measures for the evaluation of aerobic exercise training in Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) rat, a model of type 2 diabetes. The objective of this study was to assess whether aerobic exercise training may attenuate diabetes induced ECG changes.
Methods: Male ZDF (obese fa/fa) and control Zucker (lean fa/+) rats were assigned to 4 groups: sedentary control (SC), sedentary diabetic (SD), exercised control (EC) and exercised diabetic (ED). The exercised groups began 7 weeks of treadmill training after the development of diabetes in the ED group. Baseline (prior to the training) and termination measurements included body weight, heart weight, blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin levels and ECG parameters. One way repeated measures ANOVA (group) analyzed within and between subject differences and interactions. Pearson coefficients and descriptive statistics described variable relationships and animal characteristics.
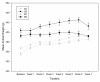
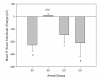
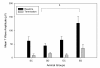
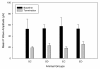
Results: Diabetes caused crucial changes in R wave amplitudes (p < 0.001), heart rate variability (p < 0.01), QT intervals (p < 0.001) and QTc intervals (p < 0.001). R wave amplitude augmentation in SD rats from baseline to termination was ameliorated by exercise, resulting in R wave amplitude changes in ED animals similar to control rats. Aerobic exercise training neither attenuated QT or QTc interval prolongation nor restored decreases in HRV in diabetic rats.
Conclusion: This study revealed alterations in R wave amplitudes, HRV, QT and QTc intervals in ZDF rats. Of these changes, aerobic exercise training was able to correct R wave amplitude changes. In addition, exercise has beneficial effect in this diabetic rat model in regards to ECG correlates of left ventricular mass.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of obesity and diabesity on heart rhythm in the Zucker rat.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2021 May;48(5):735-747. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13473. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33609055
-
Progression of vascular and neural dysfunction in sciatic nerves of Zucker diabetic fatty and Zucker rats.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Jul;289(1):E113-22. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00594.2004. Epub 2005 Feb 22. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005. PMID: 15727946
-
Exercise training decreases proinflammatory profile in Zucker diabetic (type 2) fatty rats.Nutrition. 2009 Mar;25(3):330-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2008.08.014. Epub 2008 Dec 5. Nutrition. 2009. PMID: 19062255
-
Exercise Training Attenuates the Development of Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction in Diabetic Rats.In Vivo. 2018 Nov-Dec;32(6):1433-1441. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11396. In Vivo. 2018. PMID: 30348698 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of exercise training on heart rate variability in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 May 17;16(5):e0251863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251863. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33999947 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Myocardial impulse propagation is impaired in right ventricular tissue of Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013 Jan 17;12:19. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-19. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013. PMID: 23327647 Free PMC article.
-
Diet-induced pre-diabetes slows cardiac conductance and promotes arrhythmogenesis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015 Jul 14;14:87. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0246-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015. PMID: 26169175 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise increases insulin content and basal secretion in pancreatic islets in type 1 diabetic mice.Exp Diabetes Res. 2011;2011:481427. doi: 10.1155/2011/481427. Epub 2011 Sep 11. Exp Diabetes Res. 2011. PMID: 21912535 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of β-adrenoceptor subtypes on cardiac function in myocardial infarction rats exposed to fine particulate matter (PM 2.5).Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:308295. doi: 10.1155/2014/308295. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25187901 Free PMC article.
-
Sirt1 and Sirt3 Activation Improved Cardiac Function of Diabetic Rats via Modulation of Mitochondrial Function.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 24;10(3):338. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030338. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christensen PK, Gall MA, Major-Pedersen A, Sato A, Rossing P, Breum L, Pietersen A, Kastrup J, Parving HH. QTc interval length and QT dispersion as predictors of mortality in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2000;60(4):323–332. doi: 10.1080/003655100750046486. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mathur C, Gupta D. QTc prolongation in diabetes mellitus-An indicator of cardiac autonomic neuropathy. Journal, Indian Academy Clinical Medicine. 2006;7(2):130–132.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

