The effects of oligomerization on Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mcm4/6/7 function
- PMID: 20860810
- PMCID: PMC2949612
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-11-37
The effects of oligomerization on Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mcm4/6/7 function
Abstract
Background: Minichromosome maintenance proteins (Mcm) 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 are related by sequence and form a variety of complexes that unwind DNA, including Mcm4/6/7. A Mcm4/6/7 trimer forms one half of the Mcm2-7 hexameric ring and can be thought of as the catalytic core of Mcm2-7, the replicative helicase in eukaryotic cells. Oligomeric analysis of Mcm4/6/7 suggests that it forms a hexamer containing two Mcm4/6/7 trimers, however, under certain conditions trimeric Mcm4/6/7 has also been observed. The functional significance of the different Mcm4/6/7 oligomeric states has not been assessed. The results of such an assessment would have implications for studies of both Mcm4/6/7 and Mcm2-7.
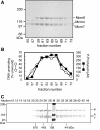
Results: Here, we show that Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mcm4/6/7 reconstituted from individual subunits exists in an equilibrium of oligomeric forms in which smaller oligomers predominate in the absence of ATP. In addition, we found that ATP, which is required for Mcm4/6/7 activity, shifts the equilibrium towards larger oligomers, likely hexamers of Mcm4/6/7. ATPγS and to a lesser extent ADP also shift the equilibrium towards hexamers. Study of Mcm4/6/7 complexes containing mutations that interfere with the formation of inter-subunit ATP sites (arginine finger mutants) indicates that full activity of Mcm4/6/7 requires all of its ATP sites, which are formed in a hexamer and not a trimer. In keeping with this observation, Mcm4/6/7 binds DNA as a hexamer.
Conclusions: The minimal functional unit of Mcm4/6/7 is a hexamer. One of the roles of ATP binding by Mcm4/6/7 may be to stabilize formation of hexamers.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Concerted loading of Mcm2-7 double hexamers around DNA during DNA replication origin licensing.Cell. 2009 Nov 13;139(4):719-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.015. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19896182 Free PMC article.
-
Dbf4 and Cdc7 proteins promote DNA replication through interactions with distinct Mcm2-7 protein subunits.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 24;288(21):14926-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.392910. Epub 2013 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23549044 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Mcm7 and Mcm4 subunits in the DNA helicase activity of the mouse Mcm4/6/7 complex.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 8;277(45):42471-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205769200. Epub 2002 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12207017
-
The hexameric eukaryotic MCM helicase: building symmetry from nonidentical parts.J Biol Chem. 2000 Nov 10;275(45):34833-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R000018200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10980206 Review. No abstract available.
-
The Eukaryotic CMG Helicase at the Replication Fork: Emerging Architecture Reveals an Unexpected Mechanism.Bioessays. 2018 Mar;40(3):10.1002/bies.201700208. doi: 10.1002/bies.201700208. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Bioessays. 2018. PMID: 29405332 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional responses of Candida glabrata biofilm cells to fluconazole are modulated by the carbon source.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2020 Jan 23;6:4. doi: 10.1038/s41522-020-0114-5. eCollection 2020. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2020. PMID: 31993211 Free PMC article.
-
DNA replication: Mechanisms and therapeutic interventions for diseases.MedComm (2020). 2023 Feb 5;4(1):e210. doi: 10.1002/mco2.210. eCollection 2023 Feb. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 36776764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression, purification and biochemical characterization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Mcm4, 6 and 7.BMC Biochem. 2013 Feb 27;14:5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-14-5. BMC Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23444842 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis thaliana MCM3 single subunit of MCM2-7 complex functions as 3' to 5' DNA helicase.Protoplasma. 2016 Mar;253(2):467-75. doi: 10.1007/s00709-015-0825-2. Epub 2015 May 6. Protoplasma. 2016. PMID: 25944245
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

