Heparan sulfate acts as a bone morphogenetic protein coreceptor by facilitating ligand-induced receptor hetero-oligomerization
- PMID: 20861306
- PMCID: PMC2982130
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-04-0348
Heparan sulfate acts as a bone morphogenetic protein coreceptor by facilitating ligand-induced receptor hetero-oligomerization
Abstract
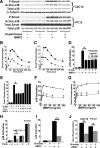
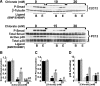
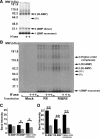
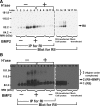
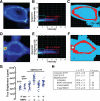
Cell surface heparan sulfate (HS) not only binds several major classes of growth factors but also sometimes potentiates their activities--an effect usually termed "coreception." A view that coreception is due to the stabilization of growth factor-receptor interactions has emerged primarily from studies of the fibroblast growth factors (FGFs). Recent in vivo studies have strongly suggested that HS also plays an important role in regulating signaling by the bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). Here, we provide evidence that the mechanism of coreception for BMPs is markedly different from that established for FGFs. First, we demonstrate a direct, stimulatory role for cell surface HS in the immediate signaling activities of BMP2 and BMP4, and we provide evidence that HS-BMP interactions are required for this effect. Next, using several independent assays of ligand binding and receptor assembly, including coimmunoprecipitation, cross-linking, and fluorescence fluctuation microscopy, we show that HS does not affect BMP binding to type I receptor subunits but instead enhances the subsequent recruitment of type II receptor subunits to BMP-type I receptor complexes. This suggests a view of HS as a catalyst of the formation of signaling complexes, rather than as a stabilizer of growth factor binding.
Figures
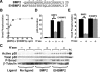
References
-
- Baeuerle P. A., Huttner W. B. Chlorate–a potent inhibitor of protein sulfation in intact cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986;141:870–877. - PubMed
-
- Belenkaya T. Y., Han C., Yan D., Opoka R. J., Khodoun M., Liu H., Lin X. Drosophila Dpp morphogen movement is independent of dynamin-mediated endocytosis but regulated by the glypican members of heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Cell. 2004;119:231–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

