The cytoprotective effects of dantrolene: a ryanodine receptor antagonist
- PMID: 20861418
- PMCID: PMC9382853
- DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181f7181c
The cytoprotective effects of dantrolene: a ryanodine receptor antagonist
Abstract
Calcium, as a second messenger, has an important role in a variety of cellular functions. However, disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis leads to cytotoxicity and cell death. Excessive calcium release from intracellular stores, via the calcium channel ryanodine receptor, contributes to cell damage. Dysfunction of calcium homeostasis is established in tissue culture and animal models of ischemia, hypoxia, seizure, trauma, anesthesia, and neurodegenerative diseases. Dantrolene, the primary drug to treat malignant hyperthermia, is a ryanodine receptor antagonist. Dantrolene inhibits abnormal calcium release from the sarco-endoplasmic reticulum, which is the primary intracellular calcium store. Dantrolene has been investigated widely for its possible cytoprotective effects against cell damage in different tissue culture or animal models of diseases involving cytotoxicity induced by disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis in pathogenesis. In this review, we summarize the role of the disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis on cell death, the pharmacologic and pharmacokinetic features of dantrolene, and the cytoprotective effects and potential application of dantrolene for the inhibition of cell damage in a wide variety of models of stress and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
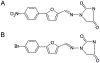
References
-
- Tsutsumi Y, Yamamoto K, Matsuura S, Hata S, Sakai M, Shirakura K. The treatment of neuroleptic malignant syndrome using dantrolene sodium. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 1998;52: 433–8 - PubMed
-
- Dykes MH. Evaluation of a muscle relaxant: dantrolene sodium (Dantrium). JAMA 1975;231:862–4 - PubMed
-
- Krause T, Gerbershagen MU, Fiege M, Weisshorn R, Wappler F. Dantrolene: a review of its pharmacology, therapeutic use and new developments. Anaesthesia 2004;59:364–73 - PubMed
-
- Hall AP, Henry JA. Acute toxic effects of ‘Ecstasy’ (MDMA) and related compounds: overview of pathophysiology and clinical management. Br J Anaesth 2006;96:678–85 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

