Lysophosphatidic Acid Upregulates Laminin-332 Expression during A431 Cell Colony Dispersal
- PMID: 20862207
- PMCID: PMC2938436
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/107075
Lysophosphatidic Acid Upregulates Laminin-332 Expression during A431 Cell Colony Dispersal
Abstract
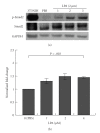
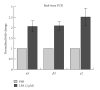
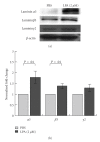
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a bioactive phospholipid that affects various biological functions, such as cell proliferation, migration, survival, wound healing, and tumor invasion through LPA receptors. Previously, we reported that LPA induces A431 colony dispersal, accompanied by disruption of cell-cell contacts and cell migration. However, it remains unclear how LPA affects cell migration and gene expression during A431 colony dispersal. In this paper, we performed cDNA microarray analysis to investigate this question by comparing gene expression between untreated and LPA-treated A431 cells. Interestingly, these results revealed that LPA treatment upregulates several TGF-β1 target genes, including laminin-332 (Ln-332) components (α3, β3, and γ2 chains). Western blot analysis also showed that LPA increased phosphorylation of Smad2, an event that is carried out by TGF-β1 interactions. Among the genes upregulated, we further addressed the role of Ln-332. Real-time PCR analysis confirmed the transcriptional upregulation of all α3, β3, and γ2 chains of Ln-332 by LPA, corresponding to the protein level increases revealed by western blot. Further, the addition of anti-Ln-332 antibody prevented LPA-treated A431 colonies from dispersing. Taken together, our results suggest that LPA-induced Ln-332 plays a significant role in migration of individual cells from A431 colonies.
Figures




Similar articles
-
GPR87 mediates lysophosphatidic acid-induced colony dispersal in A431 cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 5;715(1-3):15-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.06.029. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23831392 Review.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid activates TGFBIp expression in human corneal fibroblasts through a TGF-β1-dependent pathway.Cell Signal. 2012 Jun;24(6):1241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.02.009. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22374302
-
Increase of laminin 5 synthesis in human keratinocytes by acute wound fluid, inflammatory cytokines and growth factors, and lysophospholipids.Br J Dermatol. 2004 Nov;151(5):961-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06175.x. Br J Dermatol. 2004. PMID: 15541073
-
Cancer-derived lysophosphatidic acid stimulates differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to myofibroblast-like cells.Stem Cells. 2008 Mar;26(3):789-97. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0742. Epub 2007 Dec 6. Stem Cells. 2008. PMID: 18065393
-
Unique Biological Activity and Potential Role of Monomeric Laminin-γ2 as a Novel Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 8;20(1):226. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010226. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30626121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in Laminin Expression Pattern during Early Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 17;10(9):e0138346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138346. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26378917 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 and relation with cell proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis on preneoplastic changes induced by cadmium chloride in the rat ventral prostate.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57742. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057742. Epub 2013 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23451264 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic domain interactions of syndecan-1 and syndecan-4 with α6β4 integrin mediate human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER1 and HER2)-dependent motility and survival.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 31;289(44):30318-30332. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.586438. Epub 2014 Sep 8. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25202019 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of factors involved in apoptosis and cell survival is correlated with enzymes synthesizing lysophosphatidic acid and its receptors in granulosa cells originating from different types of bovine ovarian follicles.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2017 Sep 6;15(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12958-017-0287-9. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28874163 Free PMC article.
-
The Misregulation of Cell Adhesion Components during Tumorigenesis: Overview and Commentary.J Oncol. 2010;2010:174715. doi: 10.1155/2010/174715. Epub 2010 Sep 30. J Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20953359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Corven EJ, Groenink A, Jalink K, Eichholtz T, Moolenaar WH. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell. 1989;59(1):45–54. - PubMed
-
- Moolenaar WH, van Meeteren LA, Giepmans BNG. The ins and outs of lysophosphatidic acid signaling. BioEssays. 2004;26(8):870–881. - PubMed
-
- Gaits F, Fourcade O, Le Balle F, et al. Lysophosphatidic acid as a phospholipid mediator: pathways of synthesis. FEBS Letters. 1997;410(1):54–58. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

