Presenilin-1 regulates induction of hypoxia inducible factor-1α: altered activation by a mutation associated with familial Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20863403
- PMCID: PMC2955646
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-5-38
Presenilin-1 regulates induction of hypoxia inducible factor-1α: altered activation by a mutation associated with familial Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Mutations in presenilin-1 (Psen1) cause familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD). Both hypoxia and ischemia have been implicated in the pathological cascade that leads to amyloid deposition in AD. Here we investigated whether Psen1 might regulate hypoxic responses by modulating induction of the transcription factor hypoxia inducible factor 1-α (HIF-1α).
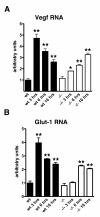
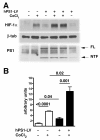
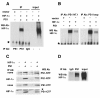
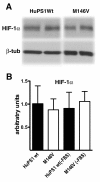
Results: In fibroblasts that lack Psen1 induction of HIF-1α was impaired in response to the hypoxia mimetic cobalt chloride, as well as was induction by insulin and calcium chelation. Reintroduction of human Psen1 using a lentiviral vector partially rescued the responsiveness of Psen1-/- fibroblasts to cobalt chloride induction. HIF-1α induction did not require Psen1's associated γ-secretase activity. In addition, the failure of insulin to induce HIF-1α was not explicable on the basis of failed activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K/Akt) pathway which activated normally in Psen1-/- fibroblasts. Rather we found that basal levels of HIF-1α were lower in Psen1-/- fibroblasts and that the basis for lower constitutive levels of HIF-1α was best explained by accelerated HIF-1α degradation. We further found that Psen1 and HIF-1α physically interact suggesting that Psen1 may protect HIF-1α from degradation through the proteasome. In fibroblasts harboring the M146V Psen1 FAD mutation on a mouse Psen1 null background, metabolic induction of HIF-1α by insulin was impaired but not hypoxic induction by cobalt chloride. Unlike Psen1-/- fibroblasts, basal levels of HIF-1α were normal in FAD mutant fibroblasts but activation of the insulin-receptor pathway was impaired. Interestingly, in Psen1-/- primary neuronal cultures HIF-1α was induced normally in response to cobalt chloride but insulin induction of HIF-1α was impaired even though activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway by insulin proceeded normally in Psen1-/- neuronal cultures. Basal levels of HIF-1α were not significantly different in Psen1-/- neurons and HIF-1α levels were normal in Psen1-/- embryos.
Conclusions: Collectively these studies show that Psen1 regulates induction of HIF-1α although they indicate that cell type specific differences exist in the effect of Psen1 on induction. They also show that the M146V Psen1 FAD mutation impairs metabolic induction of HIF-1α, an observation that may have pathophysiological significance for AD.
Figures







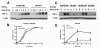





Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor by presenilin/γ-secretase loss-of-function mutations.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 30;33(5):1915-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3402-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23365231 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic condition- and high cell density-induced expression of Redd1 is regulated by activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and Sp1 through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway.Cell Signal. 2007 Jul;19(7):1393-403. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.12.014. Epub 2007 Jan 20. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17307335
-
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein level during hypoxic conditions by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase 3beta pathway in HepG2 cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 15;278(33):31277-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300763200. Epub 2003 May 22. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12764143
-
Hypoxia/ischemia activate processing of Amyloid Precursor Protein: impact of vascular dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurochem. 2017 Feb;140(4):536-549. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13932. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Neurochem. 2017. PMID: 27987381 Review.
-
HIF-1α serves as a co-linker between AD and T2DM.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Feb;171:116158. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116158. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38242039 Review.
Cited by
-
Presenilin-1 regulates the constitutive turnover of the fibronectin matrix in endothelial cells.BMC Biochem. 2012 Dec 21;13:28. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-13-28. BMC Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23259730 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Neuronal Iron Homeostasis as an Alternative Unifying Effect of Mutations Causing Familial Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2018 Aug 13;12:533. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00533. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30150923 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin-Deficient Neurons and Astrocytes Display Normal Mitochondrial Phenotypes.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jan 22;14:586108. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.586108. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33551720 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor by presenilin/γ-secretase loss-of-function mutations.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 30;33(5):1915-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3402-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23365231 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated loss of hypoxia response in zebrafish with familial Alzheimer's disease-like mutation of presenilin 1.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Aug 11;29(14):2379-2394. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa119. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32588886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 2001;81(2):741–766. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer Disease & Frontotemporal Dementia Mutation Database. http://www.molgen.ua.ac.be/ADMutations
-
- Lleo A, Berezovska O, Growdon JH, Hyman BT. Clinical, pathological, and biochemical spectrum of Alzheimer disease associated with PS-1 mutations. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2004;12(2):146–156. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

