The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the guinea pig
- PMID: 20864022
- PMCID: PMC2948547
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2010.04.015
The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the guinea pig
Abstract
Objective: This review focuses on the criteria for assessing osteoarthritis (OA) in the guinea pig at the macroscopic and microscopic levels, and recommends particular assessment criteria to assist standardization in the conduct and reporting of preclinical trails in guinea pig models of OA.
Methods: A review was conducted of all OA studies from 1958 until the present that utilized the guinea pig. The PubMed database was originally searched August 1, 2006 using the following search terms: guinea pig and OA. We continued to check the database periodically throughout the process of preparing this chapter and the final search was conducted January 7, 2009. Additional studies were found in a review of abstracts from the OsteoArthritis Research Society International (OARSI) conferences, Orthopaedic Research Society (ORS) conferences, and literature related to histology in other preclinical models of OA reviewed for relevant references. Studies that described or used systems for guinea pig joint scoring on a macroscopic, microscopic, or ultrastructural basis were included in the final comprehensive summary and review. General recommendations regarding methods of OA assessment in the guinea pig were derived on the basis of a comparison across studies and an inter-rater reliability assessment of the recommended scoring system.
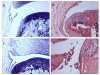
Results: A histochemical-histological scoring system (based on one first introduced by H. Mankin) is recommended for semi-quantitative histological assessment of OA in the guinea pig, due to its already widespread adoption, ease of use, similarity to scoring systems used for OA in humans, its achievable high inter-rater reliability, and its demonstrated correlation with synovial fluid biomarker concentrations. Specific recommendations are also provided for histological scoring of synovitis and scoring of macroscopic lesions of OA.
Conclusions: As summarized herein, a wealth of tools exist to aid both in the semi-quantitative and quantitative assessment of OA in the guinea pig and provide a means of comprehensively characterizing the whole joint organ. In an ongoing effort at standardization, we recommend specific criteria for assessing the guinea pig model of OA as part of an OARSI initiative, termed herein the OARSI-HISTOgp recommendations.
Copyright © 2010 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





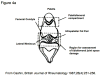

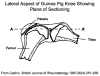
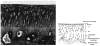
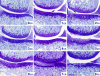


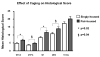
References
-
- Silverstein E, Sokoloff L. Natural history of degenerative joint disease in small animals. 5. Osteoarthritis in guinea pigs. Arthritis Rheum. 1958;1:82–86. - PubMed
-
- Bendele AM. Progressive chronic osteoarthritis in femorotibial joints of partial medial meniscectomized guinea pigs. Vet Pathol. 1987;24:444–448. - PubMed
-
- Bendele A, Hulman J. Spontaneous cartilage degeneration in guinea pigs. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:561–565. - PubMed
-
- Bendele AM, White SL, Hulman JF. Osteoarthritis in guinea pigs: histopathologic and scanning electron microscopic features. Lab Animal Sci. 1989;39:115–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

