Genetic variants influencing circulating lipid levels and risk of coronary artery disease
- PMID: 20864672
- PMCID: PMC3891568
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.201020
Genetic variants influencing circulating lipid levels and risk of coronary artery disease
Abstract
Objective: Genetic studies might provide new insights into the biological mechanisms underlying lipid metabolism and risk of CAD. We therefore conducted a genome-wide association study to identify novel genetic determinants of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and triglycerides.
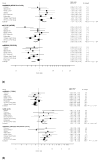
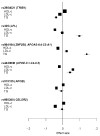
Methods and results: We combined genome-wide association data from 8 studies, comprising up to 17 723 participants with information on circulating lipid concentrations. We did independent replication studies in up to 37 774 participants from 8 populations and also in a population of Indian Asian descent. We also assessed the association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at lipid loci and risk of CAD in up to 9 633 cases and 38 684 controls. We identified 4 novel genetic loci that showed reproducible associations with lipids (probability values, 1.6×10(-8) to 3.1×10(-10)). These include a potentially functional SNP in the SLC39A8 gene for HDL-C, an SNP near the MYLIP/GMPR and PPP1R3B genes for LDL-C, and at the AFF1 gene for triglycerides. SNPs showing strong statistical association with 1 or more lipid traits at the CELSR2, APOB, APOE-C1-C4-C2 cluster, LPL, ZNF259-APOA5-A4-C3-A1 cluster and TRIB1 loci were also associated with CAD risk (probability values, 1.1×10(-3) to 1.2×10(-9)).
Conclusions: We have identified 4 novel loci associated with circulating lipids. We also show that in addition to those that are largely associated with LDL-C, genetic loci mainly associated with circulating triglycerides and HDL-C are also associated with risk of CAD. These findings potentially provide new insights into the biological mechanisms underlying lipid metabolism and CAD risk.
Figures
Comment in
-
Genome-wide association studies of plasma lipids: have we reached the limit?Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Nov;30(11):2084-6. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.214643. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20962295 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kannel WB, Dawber TR, Kagan A, Revotskie N, Stokes J., III Factors of risk in the development of coronary heart disease--six year follow-up experience. The Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med. 1961;55:33–50. - PubMed
-
- Barkowski RS, Frishman WH. HDL metabolism and CETP inhibition. Cardiol Rev. 2008;16:154–162. - PubMed
-
- Singh IM, Shishehbor MH, Ansell BJ. High-density lipoprotein as a therapeutic target: a systematic review. JAMA. 2007;298:786–798. - PubMed
-
- Smith GD, Timpson N, Ebrahim S. Strengthening causal inference in cardiovascular epidemiology through Mendelian randomization. Ann Med. 2008;40:524–541. - PubMed
-
- Kathiresan S, Willer CJ, Peloso GM, Demissie S, Musunuru K, Schadt EE, Kaplan L, Bennett D, Li Y, Tanaka T, Voight BF, Bonnycastle LL, Jackson AU, Crawford G, Surti A, Guiducci C, Burtt NP, Parish S, Clarke R, Zelenika D, Kubalanza KA, Morken MA, Scott LJ, Stringham HM, Galan P, Swift AJ, Kuusisto J, Bergman RN, Sundvall J, Laakso M, Ferrucci L, Scheet P, Sanna S, Uda M, Yang Q, Lunetta KL, Dupuis J, de Bakker PI, O’Donnell CJ, Chambers JC, Kooner JS, Hercberg S, Meneton P, Lakatta EG, Scuteri A, Schlessinger D, Tuomilehto J, Collins FS, Groop L, Altshuler D, Collins R, Lathrop GM, Melander O, Salomaa V, Peltonen L, Orho-Melander M, Ordovas JM, Boehnke M, Abecasis GR, Mohlke KL, Cupples LA. Common variants at 30 loci contribute to polygenic dyslipidemia. Nat Genet. 2009;41:56–65. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 079895/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0601966/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0701863/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 077016/Z/05/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- PG/08/094/26019/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 5R01HL087679-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106188470/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0700931/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- GR069224/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_U105630924/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 1RL1MH083268-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062418/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0500539/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_QA137934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0801566/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- PG/08/094/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

