PKC signaling regulates drug resistance of the fungal pathogen Candida albicans via circuitry comprised of Mkc1, calcineurin, and Hsp90
- PMID: 20865172
- PMCID: PMC2928802
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001069
PKC signaling regulates drug resistance of the fungal pathogen Candida albicans via circuitry comprised of Mkc1, calcineurin, and Hsp90
Abstract
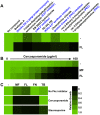
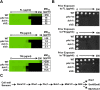
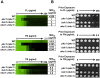
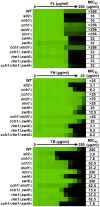
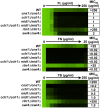
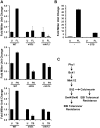
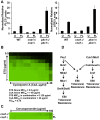
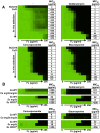
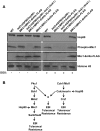
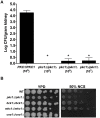
Fungal pathogens exploit diverse mechanisms to survive exposure to antifungal drugs. This poses concern given the limited number of clinically useful antifungals and the growing population of immunocompromised individuals vulnerable to life-threatening fungal infection. To identify molecules that abrogate resistance to the most widely deployed class of antifungals, the azoles, we conducted a screen of 1,280 pharmacologically active compounds. Three out of seven hits that abolished azole resistance of a resistant mutant of the model yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and a clinical isolate of the leading human fungal pathogen Candida albicans were inhibitors of protein kinase C (PKC), which regulates cell wall integrity during growth, morphogenesis, and response to cell wall stress. Pharmacological or genetic impairment of Pkc1 conferred hypersensitivity to multiple drugs that target synthesis of the key cell membrane sterol ergosterol, including azoles, allylamines, and morpholines. Pkc1 enabled survival of cell membrane stress at least in part via the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade in both species, though through distinct downstream effectors. Strikingly, inhibition of Pkc1 phenocopied inhibition of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 or its client protein calcineurin. PKC signaling was required for calcineurin activation in response to drug exposure in S. cerevisiae. In contrast, Pkc1 and calcineurin independently regulate drug resistance via a common target in C. albicans. We identified an additional level of regulatory control in the C. albicans circuitry linking PKC signaling, Hsp90, and calcineurin as genetic reduction of Hsp90 led to depletion of the terminal MAPK, Mkc1. Deletion of C. albicans PKC1 rendered fungistatic ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitors fungicidal and attenuated virulence in a murine model of systemic candidiasis. This work establishes a new role for PKC signaling in drug resistance, novel circuitry through which Hsp90 regulates drug resistance, and that targeting stress response signaling provides a promising strategy for treating life-threatening fungal infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hsp90 governs echinocandin resistance in the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans via calcineurin.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Jul;5(7):e1000532. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000532. Epub 2009 Jul 31. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19649312 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 governs dispersion and drug resistance of fungal biofilms.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002257. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002257. Epub 2011 Sep 8. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21931556 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and genomic architecture of the evolution of resistance to antifungal drug combinations.PLoS Genet. 2013 Apr;9(4):e1003390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003390. Epub 2013 Apr 4. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23593013 Free PMC article.
-
The Hsp90 Chaperone Network Modulates Candida Virulence Traits.Trends Microbiol. 2017 Oct;25(10):809-819. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.05.003. Epub 2017 May 23. Trends Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28549824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcineurin in fungal virulence and drug resistance: Prospects for harnessing targeted inhibition of calcineurin for an antifungal therapeutic approach.Virulence. 2017 Feb 17;8(2):186-197. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1201250. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Virulence. 2017. PMID: 27325145 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anticandidal Effect and Mechanisms of Monoterpenoid, Perillyl Alcohol against Candida albicans.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 14;11(9):e0162465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162465. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27627759 Free PMC article.
-
Sesamol: a natural phenolic compound with promising anticandidal potential.J Pathog. 2014;2014:895193. doi: 10.1155/2014/895193. Epub 2014 Dec 9. J Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25574401 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Synthesis of Fungal-Selective Resorcylate Aminopyrazole Hsp90 Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2020 Mar 12;63(5):2139-2180. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00826. Epub 2019 Sep 26. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31513387 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of stress signalling pathways enhances tolerance of fungi to chemical fungicides and antifungal proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Jul;71(14):2651-66. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1573-8. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24526056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking Cellular Morphogenesis with Antifungal Treatment and Susceptibility in Candida Pathogens.J Fungi (Basel). 2019 Feb 21;5(1):17. doi: 10.3390/jof5010017. J Fungi (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30795580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

