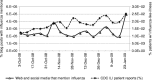
Using Web and social media for influenza surveillance
- PMID: 20865540
- PMCID: PMC7123932
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4419-5913-3_61
Using Web and social media for influenza surveillance
Abstract
Analysis of Google influenza-like-illness (ILI) search queries has shown a strongly correlated pattern with Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and Prevention seasonal ILI reporting data. Web and social media provide another resource to detect increases in ILI. This paper evaluates trends in blog posts that discuss influenza. Our key finding is that from 5th October 2008 to 31st January 2009, a high correlation exists between the frequency of posts, containing influenza keywords, per week and CDC influenza-like-illness surveillance data.
Figures
References
-
- Bailey N. The Mathematical Theory of Epidemics. London: Griffin; 1957.
-
- CDC-Website: Influenza surveillance reports. Website (accessed 25 July 2009). http://www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/fluactivity.htm
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical